
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Emerald Calloway - Economix Emerald Calloway - Economi X
← C D
→
Emerald Calloway - Economics Unit 1 Review ✩
File Edit View Insert Format Tools Extensions Help
a 5
==
■
■
Ơ
Q Search
docs.google.com/document/d/1GKw-TYD33-OEXzSCMAIMkqpsEWrSd-N53NcQ4p46qSE/edit
A
100%
Normal text
in…ட்
▼
Arial
12/6 - Unit 2 and 3 Review X
1
Toothpicks
▼
Ps
2
11 +
I
Emerald Calloway - Economi X
3
B I U A
4
G
New Tab
E▾
15
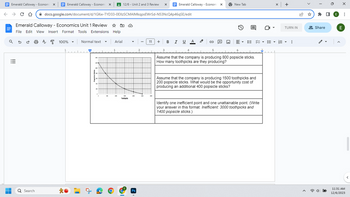
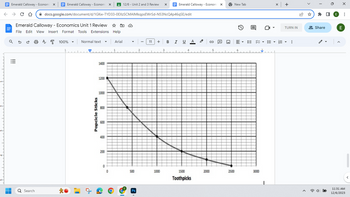
Assume that the company is producing 800 popsicle sticks.
How many toothpicks are they producing?
8
Assume that the company is producing 1500 toothpicks and
200 popsicle sticks. What would be the opportunity cost of
producing an additional 400 popsicle sticks?
Identify one inefficient point and one unattainable point. (Write
your answer in this format: Inefficient: 3000 toothpicks and
1400 popsicle sticks.)
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
x +
TURN IN
▾▾
⠀
A
Share
E
X
E
:
11:31 AM
12/6/2023
Transcribed Image Text:Emerald Calloway - Economix Emerald Calloway - Economi X
← C D
→
N-
3-
5.
Emerald Calloway - Economics Unit 1 Review ✩
File Edit View Insert Format Tools Extensions Help
a 5
■
▬
|||
Q Search
docs.google.com/document/d/1GKw-TYD33-0EXzSCMAIMkqpsEWrSd-N53NcQ4p46qSE/edit
A 100%
Normal text
Popcicle Sticks
1400
1200
▼
1000
800
600
400
200
0
0
Arial
12/6 - Unit 2 and 3 Review X
1.
500
Ps
²
11 +
13
Emerald Calloway - Economi X
1000
B I U A Ο
4
1500
Toothpicks
2000
5
New Tab
2500
8
===▼
E
3000
x +
TURN IN
▼ ▼
E
A
Share
E
X
E
:
11:31 AM
12/6/2023
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Emmanuel likes gardening. He grows zucchini that he sells at the local farmers' market. The table below describes the benefits and costs Emmanuel faces as he decides how many hours to dedicate to his garden each week. a. Complete the "Marginal Benefit" and "Marginal Cost" columns in the table below. Emmanuel's Gardening Benefits and Costs Hours Spent Gardening Total Benefit (dollars) Marginal Benefit (dollars) Total Cost (dollars) Marginal Cost (dollars) 1 $21 $ $3 $ 2 39 9 3 54 18 4 66 30 5 75 45 6 81 63 7 84 84arrow_forward1. What is meant by opportunity cost? Give an example. Suppose that you need to take a class at 3PM, but you can also work an extra shift at your job. What is the opportunity cost of taking the 3PM class?arrow_forward1 Use the equations given below and calculate total benefit, total cost, marginal benefit, and marginal cost for values of Q ranging from 35 to 45 Total Benefits: P = 314Q – 16Q Marginal Benefits: P = 314 – 32Q Total Cost: P = 50Q + 17Q Marginal Cost: P = 50 + 34Q 1) Graph total benefit and total cost on one graph, and marginal benefit and marginal cost on the other graph 2) Find the optimal value of Q and P 3) Calculate the total benefit, total cost, and net benefit at the equilibriumarrow_forward
- Would you rather have efficiency or variety? That is, one opportunity cost of the variety of products we have is that each product costs more per unit than if there were only one kind of product of a given type, like shoes. Perhaps a better question is, “What is the right amount of variety? Can there be too many varieties of shoes, for example?” the bold question i dont understadnwhat they are trying to ask me to doarrow_forwardthe data to ansSwer the questions that come after. Assignment Part I: Cassian is attending a football game at the University of Georgia It's a hot and sunny day and he is really thirsty so he decides to buy a slushie. Each slushie costs $4 at the concession stand. Complete the table and questions below. 1. What is the marginal cost of each slushie? 2 Calculate the marginal benefit from each slushie and answer Yes or No whether Cassian should purchase it. Should he purchase Total Benefit of Marginal Benefit of Quantity of Slushies the slushie? Yes or Slushies Each Slushie No 1 8. 2. 14 3. 18 4. 20 18 6. 13 3. What is the maximum number of slushies Cassian will purchase?arrow_forwardCrystal is a talented artist who sells hand-crafted goods on her website. Crystal currently crafts and sells both tea towels and baskets. She spends 8 hours a day working on crafts. The following table gives different daily output scenarios depending on how much of her time is spent on each good. BASKETS Choice (Tea towels) A B C D E 30 25 20 15 10 5 Hours Crafting 0 0 8 6 4 2 0 On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot Crystal's initial production possibilities frontier (PPF). 2 (Baskets) (Tea towels) 0 2 4 6 8 3 4 TEA TOWELS 5 4 3 6 2 1 0 Produced 7 (Baskets) 0 10 16 19 8 20 Initial PPF New PPFarrow_forward
- a. Compute the opportunity cost in forgone consumer goods (millions of pounds of butter) for each additional unit of military output produced (number of planes) using the table below: Instructions: Enter your responses as a whole number. Military output Consumer goods output Opportunity cost 0 100 1 95 2 80 b. As military output increases, opportunity cos 3 60 4 35 (Click to select) decrease remain constant increase 5 0arrow_forwarda. Calculate the opportunity cost based on the following information: Instructions: Enter your responses as a whole number. Possible Output Combinations Output per month A B D F Missiles 50 100 150 200 250 Houses 100 90 75 55 30 The opportunity cost of increasing missile production by 50 is: (such as 0 to 50, 50 to 100, 100 to 150, etc.) 2,500 houses b. Using the information presented in the table above, graph the production possibilitiles with missiles on the horizontal axis and houses on the vertical axis. Instructions: Use the tool provided 'PPC' to plot the production possibilities curve (plot 6 points total). Production Possibilities Curve PPC 120 110 - 100 - 80- 70- 00- 50 - 40- 30 - 20- 10 - 50 100 150 200 250 300 Missiles (per month) reset Houses (per month)arrow_forwardNote: The answer should be typed. Answer parts d and e.arrow_forward
- I am struggling with the graphsarrow_forwardAntarctica produces only party ice and frozen fish. The table shows the marginal benefit and marginal cost schedules for frozen fish. If Antarctica produces 37 frozen fish, the marginal benefit from frozen fish frozen fish. To achieve allocative efficiency, Antarctica must O A. is less than; decrease O B. exceeds; decrease O C. O D. exceeds; increase is less than; increase C the marginal cost of the quantity of frozen fish produced. Frozen fish (per month) 33 34 35 36 37 38 Marginal cost (packs of ice per pack of fish) Marginal benefit 53 6 5 4 3 2 3 4 20 35arrow_forward01. What is the opportunity cost of Y for PPF 1? a) ½ of X b) 2 of X c) 1/3 of X d) 3 of X e) 4/5 of Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education