
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
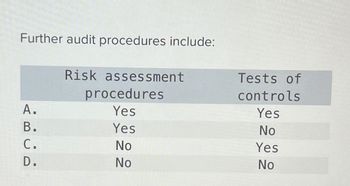
Transcribed Image Text:Further audit procedures include:
Risk assessment
procedures
Tests of
controls
A.
B.
فن فة
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
C.
No
Yes
D.
No
No
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Which of the following does not accurately summarize auditors’ requirements regardinginternal control?LO 5-5LO 5-5Management’s Report onInternal ControlAn Audit ofInternal Controla. No Nob. Yes Noc. No Yesd. Yes YesPublic Entity Nonpublic Entitya. Understanding Yes Yesb. Documenting Yes Yesc. Evaluating control risk Yes Yesd. Test controls Yes Yesarrow_forward1arrow_forwardA system audit examines the company's quality control procedures.? Question 7 options: True Falsearrow_forward
- Which of the following is correct about control risk? Select one: a. None of the others b. The risk that a material misstatement could occur in a relevant assertion and not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by the entity’s internal control. c. It is an alternative to substantive testing d. It is the same as inherent risk.arrow_forwardIf there is a detection of one control deviation, the auditor can do which of the following? a. Increase the sample size O b. Test a compensation control Oc. Amend the auditor's decision to rely on the control O d. All of the above are options for an auditor responding to detection of a control deviaticarrow_forwardIf tests of controls induce the auditor to change the assessed level of control risk for Property, Plant, and Equipment from moderate to high, and audit risk and inherent risk remain constant, the acceptable level of detection riskarrow_forward
- In a non public audit (AICPA), auditors might chose to not test controls if Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a Design of control is weak/deficient, Controls Risk is High, or High cost of testing I/C b Design of control is strong/effective, Control Risk is low or low cost of testingarrow_forwardThe difference between assessing control risk for IT control activities versus assessing control risk for manual control activities is best described as follows: Multiple Choice О in a manual environment it is important for the auditor to gain an understanding of the internal control activity before assessing control risk. О in an IT environment, it is not important to gain an understanding of the internal control activity before assessing control risk. О In an IT environment, it is likely that control risk will be assessed as low on largely all audit engagements. О the assessment process that needs to be undertaken for IT controls is essentially the same as would be taken for manual controls.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education