
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
[[
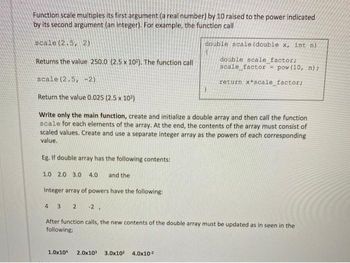
Transcribed Image Text:Function scale multiples its first argument (a real number) by 10 raised to the power indicated
by its second argument (an integer). For example, the function call
scale (2.5, 2)
double scale (double x, int n)
double scale_factor;
scale factor - pow (10, n);
return x*scale_factor;
Returns the value 250.0 (2.5 x 102). The function call
scale (2.5, -2)
Return the value 0.025 (2.5 x 10²)
Write only the main function, create and initialize a double array and then call the function
scale for each elements of the array. At the end, the contents of the array must consist of
scaled values. Create and use a separate integer array as the powers of each corresponding
value.
Eg. If double array has the following contents:
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 and the
Integer array of powers have the following:
4 3. 2 -2,
After function calls, the new contents of the double array must be updated as in seen in the
following:
1.0x104 2.0x10³ 3.0x10² 4.0x10²
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How does indexing work with columns that store JSON data in PostgreSQL?arrow_forward7. Add a foreign key constraint to the shows table: the column net_id is the foreign key, referencing the column id from the networks table. Take a screenshot now and paste it here. 8. Show the structure of your table shows. Take a screenshot now and paste it here. 9. Insert the following data in your database. You may use more than one INSERT statement. title num_episodes country start end network Daniel Tiger 105 USA 2012 NULL PBS Handy Manny 113 USA 2006 2013 Disneyarrow_forwardWhich are the benefits and drawbacks of using MySQL?arrow_forward
- 17. List the network names and the number of shows per network. Take a screenshot now and paste it here. 18. List the average number of episodes in the table shows. Take a screenshot now and paste it here. 19. List the name of the shows that have more episodes than the average number of episodes in the table shows. Use a subquery. Do not hardcode the average number (that you obtained in the previous question). Take a screenshot now and paste it here.arrow_forwardWhat does the DELETE command do in mySQL? Why is it important?arrow_forwardHow do you add a column to an existing table in MySQL? a. MODIFY TABLE table_name ADD COLUMN new_column CHAR(3); b. MODIFY TABLE table_name ADD new_column CHAR(3); c. ALTER TABLE table_name ADD new_column CHAR(3); d. ALTER TABLE table_name ADD COLUMN new_column CHAR(3);arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education