
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
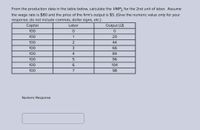
Transcribed Image Text:From the production data in the table below, calculate the VMP, for the 2nd unit of labor. Assume
the wage rate is $80 and the price of the firm's output is $5. (Give the numeric value only for your
response; do not include commas, dollar signs, etc.)
Capital
Labor
Output (Q)
100
100
1
20
100
44
100
66
100
4
84
100
96
100
104
100
7
98
Numeric Response
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ASAP!!arrow_forwardTwo points, A and B, are on an isoquant drawn with labor on the horizontal axis and capital on the ver- tical axis. The capital-labor ratio at B is twice that at A, and the elasticity of substitution as we move from A to B is 2. What is the ratio of the MRTSL, K at A versus that at B?arrow_forwardFor the cost function 125x + 375 x+7 where C is in dollars and x is the number produced in hundreds, use C(13) and MC(13) to approximate the cost of producing 1380 items. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) C(x) = Give an interpretation of the marginal cost value. At this level of production, the cost-Select- about $ per additional one hundred items.arrow_forward
- Consider a firm with Total Output function (Production Function) given by Q = 6L2 – 0.4L3, where L is variable labor input. The firm is faced with the decision to hire the optimal number of workers in order to maximize its output level. (a) Obtain the Marginal Product function. (b) Find the Average Product function. (c) Determine the level of employment that would maximize the firm’s output level. (d) Verify that the second-order condition is met for the firm's output maximum.arrow_forwardA firm uses labour, L and capital K, to produce a single product, X. capital is fixed but labour is variable. The firm’s production function is: X=-0.2L3 + 18L2 + 1620L. Where X is the number of units of the product per week, and L is the number of persons employed. A t what weekly output is marginal cost equal to average variable cost? if the price of the product is $0.20 per unit, what is the maximum weekly wage that the firm would pay rather than close down?arrow_forwardFrom your knowledge of the relationships among the various production functions, complete the following table: Variable Input L Total Product Q Average Product AP₁ Marginal Product MPL 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 30 二二二二 120 20.00 24.00 15 || 45 -15arrow_forward
- A baker uses labor (L) and raw materials (M) to produce mini Muhlenberg Mule sugar figurines (q). The process is fairly simple as workers only must make the sugar mixture and pour the mixture into the mule molds. The baker’s production function is as follows f(L, M) = L 0.50M. Let wL and wM denote the prices of a unit of L and M, respectively. (a) Write the firm’s cost minimization problem if it wants to produce q units of output. (b) Write the Lagrangian function that describes the cost minimization problem. (c) Derive the long run conditional factor input demands for L and M as a function of wL, wM, and q; L ∗ (wL, wM, q) and M∗ (wL, wM, q). (d) Suppose wL = $25 and wM = $2. Determine the cost-minimizing combination of inputs if the baker wants to produce 200 mules. (e) Using wL = $25 and wM = $2 and the demand functions from part (c), write the firm’s long run cost function CLR(q).arrow_forwardAssume there is a linear isoquant where the input combination K = 10, L = 0 produces Q = 100. Assume that this isoquant has a MRTS (marginal rate of technical substitution) such that an increase in L by 1 unit requires the firm to give up – ½ unit of K. Assume PL = $1 and PK = $1. What is the smallest total cost necessary to produce Q = 100? $20 $10 $50 $100arrow_forwardAssume there is a linear isoquant where the input combination K = 10, L = 0 produces Q = 100. Assume that this isoquant has a MRTS (marginal rate of technical substitution) such that an increase in L by 1 unit requires the firm to give up – ½ unit of K. Assume PL = $1 and PK = $1. What is the smallest total cost necessary to produce Q = 100?arrow_forward
- Known function is the production of a commodityQ = 40X + 12X2 - 1.2X3a. Calculate how many units of input X in order to achieve maximum total productb. Calculate how many units of input X in order to achieve maximum marginal productc. Calculate how many units of input X in order to achieve maximum average productarrow_forwardAssume there is a linear isoquant where the input combination K = 10, L = 0 produces Q = 100. Assume that this isoquant has a MRTS (marginal rate of technical substitution) such that an increase in L by 1 unit requires the firm to give up – ½ unit of K. Assume PL= $1 and PK = $1.What is the smallest total cost necessary to produce Q = 100?arrow_forwardAssume that total fixed costs are $46, that the average product of labor is 5 units when 10 units of output are produced, and that the wage rate is $12. If labor is the only variable input, what is the average total cost of producing 10 units of output?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education