
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
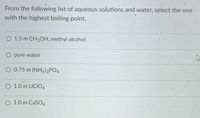
Transcribed Image Text:From the following list of aqueous solutions and water, select the one
with the highest boiling point.
O 1.5 m CH3OH, methyl alcohol
O pure water
O 0.75 m (NH4)3PO4
O 1.0 m LİCIO4
O 1.0 m CaSO4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Choose the aqueous solution below with the lowest freezing point. All solutions are made of nonvolatile solutes. These all have the same freezing point. 0.200 m Ca(ClO4)2 0.200 m C6H12O6 0.200 m Ba(NO3)2 0.200 m K3PO4arrow_forwardWhich solution has the lowest boiling point?arrow_forwardAssuming ideal behavior, which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point? O a 1.00 m NaCl Ob1.00 m Ca(NO3)2 OC 1.00 m KCIO4 Od. 1.00 m C6H1206 Oe. 1.00 m KBrarrow_forward
- A sample of an ionic solid is dissolved in 1.00 kg of water. The freezing point of the water is -0.01 °C. If three times the mass of ionic solid is dissolved in 1.00 kg of water and the resulting freezing point of the solution is -0.09 °C, which of the following would be possible formulas for the solid: MX, MX2, or MX3, where M represents a metal cation and X an anion with a 1- charge? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardLead levels in drinking water should be no higher than 15 ppb. What is this in mol/L? Assume the density of drinking water is 1.0 g/mL. O 2.0 x 10-⁹ M O 3.1 x 10 ⁹ M O 3.1 x 107 M O 7.2 x 10 8 M O 7.2 x 10 5 Marrow_forwardThe freezing point of CCI4 is -22.3°C and the freezing point depression constant is 29.8 °C/m. If a solution of C5H12 in CCI4 freezes at -37.6°C, what is the molality of this solution? O 0.513 0.722 O 2.01 O 5.01 O 1.26arrow_forward
- will have the highest boiling point. Of the following, a 0.1 m aqueous solution of NaCl O Al(NO3)3 O K2CrO4 O N22SO4 sucrosearrow_forwardAn aqueous solution of a compound used in antifreeze has an osmotic pressure of 0.589 atm at 20.0°C. It is prepared by dissolving 1.14 g of the compound in enough water to make 0.750 L of solution. What is the molar mass of the antifreeze compound? O 62.1 g/mol O 124 g/mol O 82.8 g/mol O 54.4 g/mol O 4.23 g/molarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements concerning factors that affect solute solubility is incorrect? Gaseous solutes become less soluble in water with increasing temperature Most solid solutes become less soluble in water with decreasing pressure Most Solid solute become more soluable in water with increasing temperature Gaseous solutes become more soluable in water with increasing pressurearrow_forward
- Choose the aqueous solution below with the lowest freezing point. All solutions are made of nonvolatile solutes. 0.200 m C6H12O6 0.200 m Al2(SO4)3 0.200 m K3PO4 0.200 m Ca(ClO4)2 These all have the same freezing pointarrow_forwardOrder the following four aqueous solutions by their freezing point temperature. The concentrations are in molality. Assume complete dissociation of electrolytes. highest freezing point (highest temperature) 0.035 m sucrose, C6H12O6 1 2 3 0.010 m potassium bromide, KBr 4 0.010 m sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 0.015 m calcium chloride, CaCl2 lowest freezing point (lowest temperature)arrow_forwardWhich of the following aqueous solutions has the highest osmatic pressure? 1.0 М HСIO4 0.5 M NazSO4 O 1.0 M CaCl2 2.0 M sugar O 1.0 M NaCIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY