
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
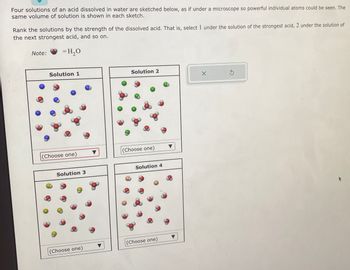
Transcribed Image Text:Four solutions of an acid dissolved in water are sketched below, as if under a microscope so powerful individual atoms could be seen. The
same volume of solution is shown in each sketch.
Rank the solutions by the strength of the dissolved acid. That is, select 1 under the solution of the strongest acid, 2 under the solution of
the next strongest acid, and so on.
= H₂O
Note:
Solution 1
(Choose one)
Solution 3
(Choose one)
Solution 2
(Choose one)
Solution 4
(Choose one)
X
Ś
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The strength of different acids can be compared on the basis of the degree of dissociation of these acids into an aqueous solution.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Four solutions of an acid dissolved in water are sketched below, as if under a microscope so powerful individual atoms could be seen. The same volume of solution is shown in each sketch. Rank the solutions by the strength of the dissolved acid. That is, select 1 under the solution of the strongest acid, 2 under the solution of the next strongest acid, and so on. =H₂O Note: Solution 1 (Choose one) Solution 3 (Choose one) Solution 2 (Choose one) Solution 4 (Choose one) X Śarrow_forward1. Part A. H3PO4 is a stronger acid than HClO4 since it has more protons. (True or False) Part B. Water is not an Arrhenius acid but can be a Bronsted acid. (True or False) Part C. A 6 M NaOH (aq) solution has no protons ions (H+) in it. (True or False)arrow_forwardA solution of HCl has a pH of 1.94. How many grams of HCl are there in 298 mL of this solution? g HCI How many grams of HCI are in 298 ml of a HCl solution that has twice the pH? g HCIarrow_forward
- plese don't handwritten solution..arrow_forwardQUES TION 4 The pH value is an expression of the molarity of H30 ions in solution. This concentration has strong impact on chemical reactions. The molarity is very small value, and therefore awkward to use. The pH scale simplifies this concentration making communication easier and faster. Demonstrate the relationship between pH and H30 molarity, using the formula, pH = -log(H30) where ) indicates concentration in molarity of a substance. What is the pH of a solution, having the H30* concentration of 0.00014 M?arrow_forwardPlz answer each partarrow_forward
- can you help me on the second problem pleasearrow_forwardEach row of the table below describes an aqueous solution at about 25 °C. Complete the table. That is, fill in any missing entries in the second and third columns. Be sure each entry you write includes the correct number of significant digits. [1,0] H,O solution pH x10 A 1.2 X 10 mol/L mol/L 10.46 0.16 mol/Larrow_forwardA solution of sodium cyanide, NaCN, has a pH of 12.00. How many grams of NaCN are in 315 mL of a solution with the same pH?arrow_forward
- For many weak acid or weak base calculations, you can use a simplifying assumption to avoid solving quadratic equations. x2 x- .2 [HА] — х [HA] Classify these situations by whether the assumption is valid or the quadratic formula is required. Assumption is valid Quadratic formula is required Answer Bank [HA] = 0.05 M Ka = 1 x 10-4 [HA] = 0.005 M Ka = 1 x 10-4 [НA] 3D 0.05 М Ka = 1 × 10-3 [HA] = = 0.005 M [HA] = 1 M Ką = 1 × 10-5 Ka = 1 × 10-3arrow_forwardEach row of the table below describes an aqueous solution at about 25 °C. Complete the table. That is, fill in any missing entries in the second and third columns. Round your entries for [H₂O*] to 2 significant digits, and your entries for pH to 2 decimal places. solution A B с [H₂O*] -6 6.5 × 10 mol/L mol/L 8 6.6 X 10 mol/L pH 0 9.24 0 x10 X Śarrow_forwardWhat salt is produced when each of the following acids and bases are mixed. Sodium HydroxideNaOHmixed with perchloric acidHClO4. Potassium hydroxideKOHmixed with hydrobromic acidHBr. Calcium hydroxideCa (OH)2mixed with hydrochloric acidHCl.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY