
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
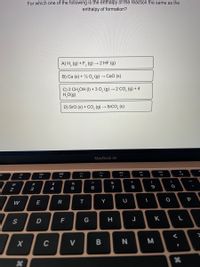
Transcribed Image Text:For which one of the following is the enthalpy of the reaction the same as the
enthalpy of formation?
A) H, (9) + F, (g)
-2 HF (g)
B) Ca (s) + ½ 0, (g) → CaO (s)
C) 2 CH,OH (1) + 3 0, (g) → 2 CO, (g) + 4
H,O(g)
D) Sro (s) + CO, (g) →
→ SrCO, (s)
MacBook Air
DI
80
888
F7
F5
F3
F4
F2
&
#3
3
@
$
%
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
P
W
E
R
Y
F
J
K.
D
C
V
B N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Standard Enthalpies NH3: -45.9 O2: 0 N2O: 81.6 H2: 0 O: 249.2 kj/mol Fe2CO3: -824.2 Fe: 0arrow_forwardA scientist measures the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction to be 209.4 kJ : CHĄ(g) + H20(g)3H2(g) + CO(g) Based on this value and the standard enthalpies of formation for the other substances, the standard enthalpy of formation of CH4(g) is kJ/mol.arrow_forwardEthylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, is used as antifreeze. It is produced from ethylene oxide, C2 H40, by the reaction C2 H4O(g) + H,0(1) HOCH, CH,OH(!) Use Hess's law to obtain the enthalpy change for this reaction from the following enthalpy changes: 2C, HO(g) + 502(9) → 4CO2 (9) + 4H,0(1) AH =-2612.2 kJ HOCH, CH, OH(1) + O2 (9) → 2002 (9) + 3H,0(1) AH=-1189.8 kJ Enthalpy change = kJ %3Darrow_forward
- Given the two thermochemical equations below, find the enthalpy change for the reaction: N2H4 (l) + H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) delta H = ? Given: N2O4 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) + 2 O2 (g) delta H = – 100.96 kJ N2O4 (g) + 2 H2 (g) → N2H4 (l) + 2 O2 (g) delta H = + 41.47 kJ Select one: a. – 142.43 kJ b. – 59.49 kJ c. + 41.47 kJ d. + 59.49 kJ e. + 142.43 kJ f. none of these g. – 100.96 kJarrow_forwardA scientist measures the standard enthalpy change for this reaction to be -739.4 kJ/mol:2CO(g) + 2 NO(g)2CO2(g) + N2(g)Based on this value and the standard formation enthalpies for the other substances, the standard formation enthalpy of CO(g) isarrow_forwardUsing the standard enthalpies of formation, what is the standard enthalpy of reaction? CO(g) + H,O(g) –→ CO,(g) + H,(g) AHân = kJarrow_forward
- Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. A scientist measures the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction to be -103.2 kJ: 4HCl(g) + O2(g) → 2H₂O(g) + 2Cl₂ (g) Based on this value and the standard enthalpies of formation for the other substances, the standard enthalpy of formation of HCl(g) is I kJ/mol red Species AH (kJ/mol) H₂O(g) -241.8 Cl₂(g) 0.0 0₂ (9) 0.0arrow_forwardA scientist measures the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction to be -912.5 kJ:2NH3(g) + 3 N2O(g)4N2(g) + 3 H2O(g)Based on this value and the standard enthalpies of formation for the other substances, the standard enthalpy of formation of H2O(g) is kJ/mol.arrow_forward(1)Consider the reaction: 2A (g) + 3 B (g) → 2 C (g) ΔHrxn = +254.3 kJ What will be the enthalpy change (in kJ) if 0.471 mol B reacts in excess A? (2)Consider the reaction: C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ΔHrxn = -393.5 kJ What mass of carbon (in g) must be reacted via this mechanism to release 581.2 kJ of heat?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY