
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
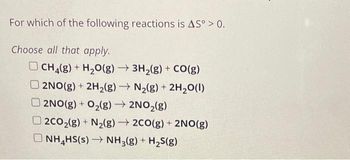
Transcribed Image Text:For which of the following reactions is AS° > 0.
Choose all that apply.
CH₂(g) + H₂O(g) → 3H₂(g) + CO(g)
2NO(g) + 2H₂(g) → N₂(g) + 2H₂O(l)
2NO(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g)
2CO₂(g) + N₂(g) → 2CO(g) + 2NO(g)
ONH₂HS(s)→ NH3(g) + H₂S(g)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ■ The disorder in a solid is greater than that in a liquid. ( ✓ or X ) ■ The tendency of a process to occur naturally is called equilibrium. (✓ or X ) ▪ A spontaneous change happens unidirectional or in one way. For a reverse change to occur, work always has to be done. (✓ or X) ■ For a spontaneous change to occur, time is not a factor. A spontaneous reaction can be a rapid or very slow reaction. (✓or X ) ■ If the system is not in the equilibrium, a spontaneous change is unavoidable. The change will continue until the system reaches the state of equilibrium. (✓or X ) ■ Thermal heat transfers between cold and hot reservoirs in both directions. (✓ or X ) ■ Absolute zero kelvin is attainable. (✓or X)arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction at 25 °C: 3 Ni(s) + N₂(g) + 3 H₂O(g) → 3 NiO(s) + 2 NH3(g) If AG° = 18.1 kJ/mol, determine the value of AG assuming that a mixture contains 57.6 g of NiO, 182.3 g of Ni, 0.24 atm of NH3, 8.54 atm of N₂ and 10.07 atm of H₂O.arrow_forwardFor which of the following reactions, carried out at constant temperature and pressure does AU = AH? Note: You may ignore work which is not related to gasses. Oa. 2HCI(g) + Mg(s) → MgCl2(s) + H2(g) Ob. O2(g) + N2O5(g) → O3(g) + N½O4(g) Oc. HCI(g) + NH3(g) – NH,CI(s) Od. H20(1) + CaC2(s) → C2H2(g) + Ca(OH)2(s) Oe. 20O2(g) + 4H2O(g) – 302(g) + 2CH;OH()arrow_forward
- A student dissolves 10.9 g of ammonium chloride (NH,Cl) in 200. g of water in a well-insulated open cup. She then observes the temperature of the water fall from 20.0 °C to 16.1 °C over the course of 3.8 minutes. Use this data, and any information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: NH,CI (s) → NH (aq) + Cl¯(aq) You can make any reasonable assumptions about the physical properties of the solution. Be sure answers you calculate using measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced students: it's possible the student did not do the experiment carefully, and the values you calculate may not be the same as the known and published values for this reaction. Ar exothermic Is this reaction exothermic, endothermic, or neither? endothermic neither If you said the rea heat that was released or absorbed by the reaction in this case. I kJ ion was exothermic or endothermic, calculate the amount of kJ…arrow_forwardA student dissolves 11.8 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH)in 250. g of water in a well-insulated open cup. She then observes the temperature of the water rise from 20.0 °C to 33.6 °C over the course of 8 minutes. Use this data, and any information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: NaOH(s) Na (aq) + OH (ag) You can make any reasonable assumptions about the physical properties of the solution. Be sure answers you calculate using measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced students: it's possible the student did not do the experiment carefully, and the values you calculate may not be the same as the known and published values for this reaction. Is this reaction exothermic, endothermic, or neither? If you said the reaction was exothermic or endothermic, calculate the amount of heat that was released or absorbed by the reaction in this case. Calculate the reaction enthalpy AH per mole of NaOH. O…arrow_forwardWhich one of the following reactions cannot proceed spontaneously as written at any temperature? Assume that ΔH°rxn does not depend on temperature. A. 2Cl2O(g) → 2Cl2(g) + O2(g) ΔH°rxn = –151 kJ B. 3O2(g) → 2O3(g) ΔH°rxn = +284 kJ C. COCl2(g) → CO(g) + Cl2(g) ΔH°rxn = +112 kJ D. 2C(s) + 2S(s) + O2(g) → 2COS(g) ΔH°rxn = –137 kJ E. N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g) ΔH°rxn = +171 kJarrow_forward
- Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction at 25 °C. Standard enthalpy of formation values can be found in this list of thermodynamic properties. MgCl₂ (s) + H₂O(1) AH;xn= V → B MgO(s) + 2 HCl(g) MacBook Air H N M 1 9 DD $10 P m kJarrow_forwardCalculate ∆H for the reaction below using Hess’s law.arrow_forwardWhat is AS for the combustion of propane? C3H8(g) +502(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H₂O(g) Substance C3H8(g) O2(g) CO2(g) H₂O(g) S(J/K mol) 269.9 205.0 213.6 188.7arrow_forward
- Calcium ΔHof (kJ/mol) ΔGof (kJ/mol) So (J/mol K) Ca (s) 0 0 41.4 Ca (g) 178.2 144.3 158.9 Ca2+ (g) 1925.9 CaC2 (s) -59.8 -64.9 70.0 CaCO3 (s, calcite) -1206.9 -1128.8 92.9 CaCl2 (s) -795.8 -748.1 104.6 CaF2 (s) -1219.6 -1167.3 68.9 CaH2 (s) -186.2 -147.2 42.0 CaO (s) -635.1 -604.0 39.8 CaS (s) -482.4 -477.4 56.5 Ca(OH)2 (s) -986.1 -898.5 83.4 Ca(OH)2 (aq) -1002.8 -868.1 -74.5 Ca3(PO4)2 (s) -4126.0 -3890.0 241.0 CaSO4 (s) -1434.1 -1321.8 106.7 CaSiO3 (s) -1630.0 -1550.0 84.0 Carbon ΔHof (kJ/mol) ΔGof (kJ/mol) So (J/mol K) C (s, graphite) 0 0 5.7 C (s, diamond) 1.9 2.9 2.4 C (g) 716.7 671.3 158.1 CCl4 (l) -135.4 -65.2 216.4 CCl4 (g) -102.9 -60.6 309.9 CHCl3 (l) -134.5 -73.7 201.7 CHCl3 (g) -103.1 -70.3 295.7 CH4 (g) -74.8 -50.7 186.3 CH3OH (g)…arrow_forwardAnswer this question without using numbers from the book (or anywhere else!) ΔS for the following reaction is negative. True or false? 2 CO(g) + O2(g) → 2 CO2(g)arrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the two reactions shown in the table below. In each case, she fills a reaction vessel with some mixture of the reactants and products at a constant temperature of 129.0 °C and constant total pressure. Then, she measures the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS of the first reaction, and the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction free energy AG of the second reaction. The results of her measurements are shown in the table. Complete the table. That is, calculate AG for the first reaction and AS for the second. (Round your answer to zero decimal places.) Then, decide whether, under the conditions the engineer has set up, the reaction is spontaneous, the reverse reaction is spontaneous, or neither forward nor reverse reaction is spontaneous because the system is at equilibrium. AH = -92. kJ J - 197. K AS = ? N, (g) + 3H, (g) 2NH, (3) AG = ||| kJ 2 Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neitherarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY