
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 16
For which of the following pairs is having nails most likely to be a homologous resemblance (one inherited from a shared
ancestor) between the two?
a. Lemur and human
O b. Tarsipes and human
Oc. Tarsipes and baboon
O d. Tarsipes and lemur
O e. There is not enough information to say
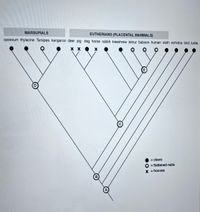
Transcribed Image Text:MARSUPIALS
EUTHERIANS (PLACENTAL MAMMALS)
opossum thylacine Tarsipes kangaroo deer pig dog horse rabbit treeshrew lemur baboon human sloth echidna bird turtle
хх
= claws
O = flattened nails
x = hooves
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are studying the skeleton and bone morphology across reptiles. You find that in alligators a certain bone in the jaw has elongated whereas in a species of chameleon the bone has shortened in the jaw. In both species the bone still helps control feeding. Is this bone and skeletal morphology a homology? a. Yes, it is a homology b. No, it is not a homology c. Not enough information to tell d. The answer depends on the specific diet of each speciesarrow_forwardCephalopods have complex eyes that arose separately from vertebrate eyes that are also used in vision. What's this an illustration of? A. Analogous structures B. Vestigial structures C. Homologous structures D. Missing linksarrow_forward1. For the skeleton characteristics, determine which of the two alternative trees you were assigned was the most parsimonious. Did the traits you chose to examine help make either of these trees more parsimonious than another? 2. Explain the evolutionary changes that happen on your most parsimonious tree.arrow_forward
- The skull pictured here represents the species: A. Pongo pygmaeus B. Paranthropus boisei C. Homo Neanderthalensis D. Pan troglodytes E. Homo erectusarrow_forwardDespite the differences in neck length, mice, humans, and giraffes all have seven cervical vertebrae. This is an illustration of A. missing links. B. homologous structures. C. vestigial structures. D. analogous structures.arrow_forwardThe size of the head of the femur reflects the magnitude of force normally applied across the joint during locomotion as well as the contribution of body mass. Using these rationales, early hominin femoral heads are absolutely ____ in diameter than Homo sapiens, and their body weight is estimated at approximately ____. a. larger, 60kg-150kg b. smaller; 60kg-150kg c. larger; 25-50kg d. smaller; 25-50kgarrow_forward
- Which species has the least robust brown ridges? A.Homo habilis B.Homo rudolfensis C.Homo erectus D.Australopithecus afarensisarrow_forwardWhat skeletal traits does P. cookie share with modern primates? A. Grasping finger B. Being a biped C. Nails D. Postorbital platearrow_forwardIn your Introduction to Biological Anthropology class, your instructor asks you to examine a fossil skull and determine which species it is. You note there is a sagittal keel at the top of the skull. Based on this information alone, to which species does the skull belong? A. Australopithecus boisei B. Homo habilis C. Australopithecus garhi D. Homo erectusarrow_forward
- Differentiate Australopithecus afarensis from Australopithecus africanus. Basis A. afarensis A. africanus a. Discoverer b. cultural means of adaptation c. diet d. greatest achievement e. size of the skull f. brain mass g. timeline of survival on earth h. specific habitat i. height and sizearrow_forward40arrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT an ancestral trait in primates? A. Trichromacy B. Having Nocturnal Adaptations C. Fur D. Clawsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education