
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
For the velocity profile shown find
1.The total displacement ,D(in):
2.The average speed,S(in/s):
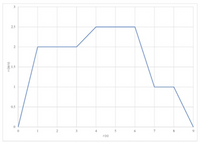
Transcribed Image Text:3
2.5
1.5
1
0.5
1
3.
4
6.
7
t(s)
v (in/s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Water enters a fountain through a pipe with a cross-sectional area A1 at a flow rate Q. The pressure in the inlet pipe is p1. The water then leaves through a nozzle with a cross sectional area A2 and at an angle 8, as shown in Figure Q5. Both the inlet and the nozzle are at a height h2, and the jet reaches a maximum height 13. You may assume that viscosity is negligible. a) Find the horizontal force on the block b) What is the horizontal-component (u2), vertical component (v2) and magnitude (V2) of the velocity of the jet as it leaves the nozzle? c) What is the maximum height of the jet? You may assume that the horizontal component of velocity is the same at every point in the jet. P₁ A₁ A₂. To h₂ h3 Figure Q5: Jet emitting from a fountain.arrow_forwardTake the densilty and pressure values at 7km, and then apply Bernoulli equation. I think this is the method to solve the problem,If there any you can proceed with that. Please do it fast ,Very urgent. Question 1: . Consider an airplane flying at a standard altitude of 7 km with a velocity of 300 m/s. At a point on the wing of the airplane, the velocity is 400 m/s. Calculate the pressure at this point.arrow_forward2%Y\ li. 1:18 HW4.png > The x- and y-motions of guides A and B with right- angle slots control the curvilinear motion of the con- necting pin P, which slides in both slots. For a short interval, the motions are governed by x 20 +t and y = 15 - , where x and y are in millimeters and t is in seconds. Calculate the magnitudes of the velocity v and acceleration a of the pin for t = 2 s. Sketch the direction of the path and indicate its cur- vature for this instant. A IIarrow_forward
- The data presented in the figure shows a generic 2.5MW wind turbine power curve and a wind speed data at hub height. 2500 0.25 2000 0.20 1500 0.15 1000 0.10 50 0.05 0.00 o 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Wind speed (m/s) wWind speed frequency Power generated by wind turbine Estimate the Annual Energy Production that this wind turbine is able to generate. Power (MW) ksuanbay paads puMarrow_forwardPlease explain on how to get the theta, Qin and Qout. It should be theta = 54.2461 deg Q in = 0.0382 m3/s Q out = 0.0191 m3/s my professor said. but I don't have solution. used 9.807m/s² not 9.81.. thank youarrow_forward1. A piston-cylinder is producing a viscous oil flow, which has the flow rate of Q, radius R=1.5 mm, and stroke L-5 mm. The fluid density is p = 800 kg/m³ and the viscosity is μ = 0.5 Pa-s. The pressure to drive the flow is p=6.25 Pa. a. How many non-dimensional groupings can be obtained? Derive them. b. If the flow transitions at Re = PV(2R) =2300. Is the generated flow laminar or turbulent given Q=20 mL/s? LL c. Assume the pressure gradient is uniform on the cross-section and can be calculated using OP=-. The velocity profile in the cylinder is u(r) = ax - [1-(²]. Sketch the velocity profile. Calculate the shear stress at the R² ap 2UÔI cylinder wall and label the direction. d. Calculate the flow rate Q with the velocity profile in (c).. e. If the shear stress is uniform over the cross-section, i.e. T = C, what's the pressure gradient distribution and sketch it? L L. Rarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY