
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
For the three cases shown below, assuming the displacement is 4.0 m to the right. Match the answers with questions.
|
|
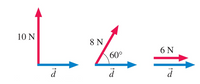
Transcribed Image Text:The image consists of three vector diagrams, each depicting forces labeled with magnitudes and directions in relation to a common direction represented by the vector \(\vec{d}\).
1. **First Diagram:**
- A red arrow pointing vertically upwards with a magnitude of 10 N.
- A blue arrow pointing horizontally to the right, labeled \(\vec{d}\).
- The red arrow is perpendicular to the blue vector \(\vec{d}\).
2. **Second Diagram:**
- A red arrow inclined at a 60° angle above the horizontal blue vector \(\vec{d}\).
- The magnitude of the red arrow is 8 N.
- The blue vector is horizontally aligned to the right.
3. **Third Diagram:**
- Both the red and blue arrows are horizontally aligned to the right.
- The red arrow has a magnitude of 6 N.
- The blue vector is labeled \(\vec{d}\).
These diagrams illustrate vector addition and the components of forces in different directions.
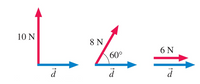
Transcribed Image Text:The image displays three vector diagrams illustrating forces acting on a vector \(\vec{d}\).
1. **First Diagram**:
- A red arrow of magnitude 10 N is pointing vertically upwards.
- The blue arrow \(\vec{d}\) is oriented horizontally to the right.
2. **Second Diagram**:
- A red arrow of magnitude 8 N forms a 60° angle above the horizontal axis.
- The blue arrow \(\vec{d}\) is oriented horizontally to the right.
3. **Third Diagram**:
- A red arrow of magnitude 6 N is directed horizontally to the right.
- The blue arrow \(\vec{d}\) is oriented in the same direction as the red arrow, horizontally to the right.
Each diagram highlights various force vectors interacting with the vector \(\vec{d}\), emphasizing the angles and magnitudes involved in vector addition and resolution.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- C7 8.) When a force acts on an object from an angle other than either 0° or 180° to the direction of motion: a.) The force is perpendicular to the direction of motion, so no work gets done. b.) The force is not in the direction of motion, so no work gets done. c.) The perpendicular vector component of the force does work but the parallel one does not. d.) The parallel vector component of the force does work but the perpendicular one does not. e.) The parallel and perpendicular component of the force both do work.arrow_forwardA 5.00 gram bullet moving horizontally with a speed of 400 m/s collides with a wooden block. After moving 2.00 cm into the block the bullet stops moving. Was work done on the bullet? If so describe the type of work and the force that did the work. a. yes, negative work, force is in the opposite direction as the initial velocity of the bullet b. yes, positive work, force is in the same direction as the initial velocity of the bullet c. yes, positive work, force is in the opposite direction as the initial velocity of the bullet d. No work was done on the bullet e. yes, negative work, force is in the same direction as the initial velocity of the bulletarrow_forwardJack and Jill ran up the hill at 2.9 m/s. The horizontal component of Jill's velocity vector was 2.5 m/s a. What was the angle of the hill? b.arrow_forward
- What is the minimum amount of work needed to lift a 3 kg box 2 meters? a. 60 J b. 5 J c. 15 J d. 120 J e. 180 Jarrow_forward1. A 50 kg sled is pushed by applying a force F = 400 N, as shown, with = 30°. The surface is rough with 4 =.4. If the sled is being displaced a distance of 60 m, find the work done on the sled by: a. An applied force F. b. The dissipative force. c. The normal force. d. The weight. F. e. The net force.arrow_forwardquestion 8arrow_forward
- please explain this in depth question 13 only and there is work done on the right but i dont really understand it. why on the right hand side does 5 turn into 5/s what makees that happen. just one specific question i hope u can explain along with the rest of the problemarrow_forwardQuestion 23 A 5.0-kg block that initially has a speed of 6.0 m/s is moving in a straight line on a level surface where there is kinetic friction between the block and the surface. What is the magnitude of the work done by the frictional force after the block comes to rest? O out of 4 points Answers: a, 210 J b. 120 J c. 150 J d. 90 J e. 180 Jarrow_forwardA box is moving along a straight line on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. The force of kinetic friction is 25 N. The initial kinetic energy of the box is 300 J. Due to the friction, the box comes to a stop. Question: What is the stopping distance? a. 4 m b. 25 m c. 30 m d. 12 marrow_forward
- For the three cases shown below, assuming the displacement is 4.0 m to the right. Match the answers with questions. 10 N 8 N 6 N 60° the work done by the 10-N force + the work done by the 8-N force + the work done by the 6-N force A. OJ В. 32J С. 16] D. 40J Е. 24]arrow_forwardWhich one of the following is equivalent to a watt? O a. N.m2 O b. N.m O c. J.s O d. N.m.s1arrow_forwardA 500 kg cart rests atop a hill 30.0 m high on a roller coaster. Its gravitational potential energy is measured relative to the bottom of the hill. The cart then rolls down the hill. Which of these best describes what is happening in this situation? a. the total mechanical energy of the cart is decreasing, the kinetic energy of the cart is increasing, and the gravitational potential energy of the cart is increasing b. the total mechanical energy of the cart is increasing, the kinetic energy of the cart is increasing, and the gravitational potential energy of the cart is increasing c. the total mechanical energy of the cart is increasing, the kinetic energy of the cart is increasing, and the gravitational potential energy of the cart is decreasing d. the total mechanical energy of the cart is increasing, the kinetic energy of the cart is decreasing, and the gravitational potential energy of the cart is increasing e. the total mechanical energy of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON