
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
(Compute) What is the scalar projection of force F, in units of lbs, along (or parallel to) position
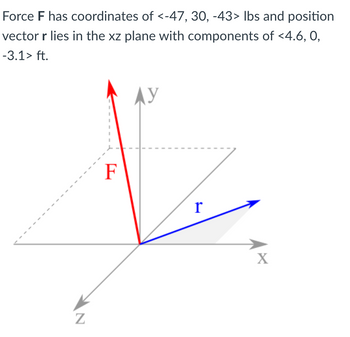
Transcribed Image Text:Force F has coordinates of <-47, 30, -43> lbs and position
vector r lies in the xz plane with components of <4.6, 0,
-3.1> ft.
Z
F
r
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
For the Scalar projection of F along r = F * Ur
How did you get the -41.924 + 24.0327
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
For the Scalar projection of F along r = F * Ur
How did you get the -41.924 + 24.0327
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the vectors Shown, analytycally determine the resultant and direction. R = A + Barrow_forwardPart I. Shorter problems focused on the fundamentals a. For the image at the right the coordinate angles are a = 63°, ẞ= 129°, y=44°. What is the unit vector? b-b Y a b. What is the Force vector in cartesian form if the magnitude of the force is 3 lb? yarrow_forwardThe traffic light shown below is supported by a system of cables. Points A and B are in a vertical plane which is parallel to the x-z plane. Point C is in the y-z plane. B Z X The traffic light has a mass of 75 kg The distances are: a = 4m, b = 6 m, c = 9 m, h = 6 m To answer the next set of questions you will determine the following: a. Position vectors for OA, OB, OC b. Unit vectors for OA, OB, OC c. Overall equilibrium equation d. Equilibrium equations in each of the x, y and z directions e. The tensions in the cables OA, OB and OC The traffic light has a mass of 75 kg. The distances are: a = 4 m, b = 6 m, c = 9 m, h = 6 m. Determine the position vector for OA. The position vector FOA can be written in the form: TOA = TOAzi+TOAİ+TOA-k You will have to input each of these three components separately below. Given: • The x component of the position vector,IOA = 4 m. • They component of the position vector,TOA = -9 m. 1. What is the z component of the position vector,TOA? Please report…arrow_forward
- Consider (Figure 1). Assume F-300 lb. Figure 4 ft 1 ft 4 ft 0 F B 2 ft ▼ Part A Determine the moment of force F about point O. Express the result as a Cartesian vector. Enter the z, y and 2 components of the moment of force separated by commas. Express your answers in pound-feet to three significant figures. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Mo = Submit ΤΟΠΙ ΑΣΦ | 17 Provide Feedback Ivec A → C ? neviem lb-ft Next >arrow_forward(a) Suppose you know the coordinates of two points A and B. How do you determine the scalar components of the position vector of point B relative to point A? (b) During the construction of a bridge, a bracket shown in Figure 1 was used to temporarily hold two cables FA and Fg = 600 N. After a while, you noticed that the bracket is shaking and slowly being pulled out of the wall by the cables. Given that e = 20°, find the resultant force and its direction counter clockwise from the positive y axis. FA 700 N 30 A Figure 1arrow_forwardFigure 1 (ii) For the system shown in Figure 2, determine (i) the required value of a if resultant of three forces is to be vertical and (ii) the corresponding magnitude of resultant. 200 N CX Figure 2 Ja 30⁰ 150 N 100 Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY