
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
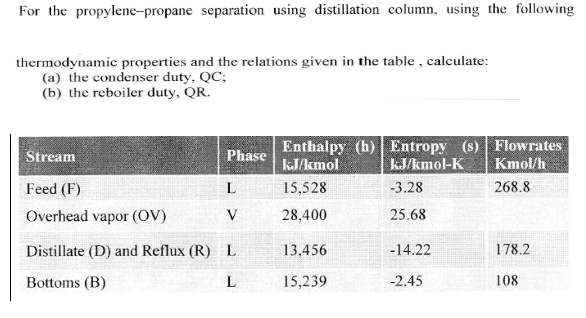
Transcribed Image Text:For the propylene-propane separation using distillation column, using the following
thermodynamic properties and the relations given in the table, calculate:
(a) the condenser duty, QC;
(b) the reboiler duty, OR.
Phase Enthalpy (h) Entropy (s) Flowrates
Stream
Feed (F)
Overhead vapor (OV)
Distillate (D) and Reflux (R)
Bottoms (B)
15,528
28,400
13,456
15,239
kJ/kmol-K Kmol/h
3.28
25.68
-14.22
-2.45
268.8
L
178.2
108
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a chemical processing plant, you are tasked with designing a cylindrical pipe system for transporting a high-temperature fluid. The pipes are made of stainless steel and are insulated with a layer of fiberglass. Considering one-dimensional heat transfer, how would you calculate the rate of heat loss from the fluid to the surroundings? Discuss the factors that would affect this heat loss and the implications for the efficiency and safety of the process. Include in your discussion the concepts of thermal conductivity, convection, and radiation, and how they interact in this scenario.arrow_forwardConsider how the Beer Heater impacts multiple aspects of distillation columns used in the bourbon industry. In these continuous distillation columns, name three three parameters that are coupled with each other?arrow_forwardo, Lateral dispersion coefficient (m) 10 5 2 10° 2 102 10' 2 5 A 700 MW coal fired power plant located in a rural area has the following operation parameters: Fuel consumption Sulphur content of coal Stack height stack diameter Stack effluent velocity Effluent temperature Ambient temp. at stack top 340 kg of coal/MW hour 3 percent 40 m / 6 m 9.5 m/sec 135°C 10°C At night with clear sky the wind speed at a height of 10m is 2.8m/s. Determine: 1. the plume rise, 2. ground level plume centreline concentration at a downwind distance of 1 km, 3. maximum ground level concentration. The following data will be useful for your calculation: For stable condition: S = g 60 Tôz 4 10² 2 5 10³ 0.33 Ah = 2.6 F₁₂ uS = 6.23 x 104 3 x 10³ 2 ,,Vertical dispersicon coefficient (m) 10' 2 102 10' 5 2 5 5 1 5 101 2 5 10% 10² 2 5 103 2 5 2 Distance from source (m) 10* Distance from source (m) 2 5 10arrow_forward
- 3 An electrical current of 700 A flows through a stainless steel cable having a diameter of 5 mm and an electrical resistance of 6 x 104 /m (i.e., per meter of cable length). The cable is in an environment having a tem- perature of 30°C, and the total coefficient associated with convection and radiation between the cable and the environment is approximately 25 W/m².K. (a) If the cable is bare, what is its surface temperature? (b) If a very thin coating of electrical insulation is applied to the cable, with a contact resistance of 0.02 m² K/W, what are the insulation and cable surface temperatures? (c) There is some concern about the ability of the insula- tion to withstand elevated temperatures. What thick- ness of this insulation (k = 0.5 W/m .K) will yield the lowest value of the maximum insulation temper- ature? What is the value of the maximum tempera- ture when this thickness is used? Note: The 25 W/m²K includes not only convection but also radiation.arrow_forwardplz write neatly, do not copy and paste solutionarrow_forwardplease show how to derive h using nusselt equation and solve for qheatlossarrow_forward
- 2 A wire of diameter D = 2 mm and uniform temperature T has an electrical resistance of 0.01 N/m and a current flow of 20 A. (a) What is the rate at which heat is dissipated per unit length of wire? What is the heat dissipation per unit volume within the wire? (b) If the wire is not insulated and is in ambient air and large surroundings for which T = Tsur = 20°C, what is the temperature T of the wire? The wire has an emissivity of 0.3, and the coefficient associated with heat transfer by natural convection may be approximated by an expression of the form, h = C[(T-T)/D]¹/4, where C = 1.25 W/m7/4.K5/4 (c) If the wire is coated with plastic insulation of 2-mm thickness and a thermal conductivity of 0.25 W/m.K, what are the inner and outer surface temperatures of the insulation? The insulation has an emissivity of 0.9, and the convection coefficient is given by the expression of part (b). Explore the effect of the insu- lation thickness on the surface temperatures. Note: 1. The metal wire…arrow_forward1. Liquid oxygen is stored in a spherical tank with D = 5 ft. The surface of the tank was isolated with insulation material A with a thickness of 8 in and outside with material B with a thickness of 0.5 ft (kA = 0.022 Btu / j.ft.oF and kB = 0.04 Btu / j.ft.oF). Tank surface temperature (–4) oC and insulation surface temperature 50oC Calculate heat transfer from air to liquid oxygen tank! 2. A 2.0 inch Schedule 40 pipe has k = 27 Btu / h.ft.oF. The fluid in the pipe has h = 30 Btu / h.ft2.oF. The outer surface of the pipe is coated with a fiber glass insulation thickness of 4 mm with k = 0.023 Btu / h.ft.oF. The convection coefficient on the outer surface of the insulation is 2.0 Btu / h.ft2.oF. The temperature of the fluid contained in the pipe is 320oF and the ambient temperature is 70oF. Calculate the heat loss per unit length of pipe! 3. Two parallel plates with a diameter of 60 cm, separated at a distance of 15 cm. The temperature on the top surface is 4 oC and the temperature on…arrow_forwardWhen using a propane tank to light fuel in a camp stove or backyard grill, the propane tank will get cold. How is this the same as what occurs at the expansion valve?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The