
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
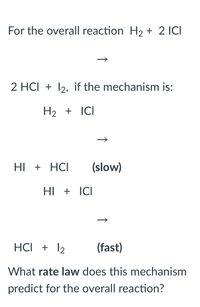
Transcribed Image Text:For the overall reaction H2 + 2 ICI
2 HCI + 12, if the mechanism is:
H2 + ICI
HI + HCI
(slow)
HI + ICI
HCI + 12
(fast)
What rate law does this mechanism
predict for the overall reaction?
![O Rate
k [HI][ICI]
Rate =
k [H2][ICI]² [HI]
O Rate
k [H2][ICI]
[HCI]²[I2]
Rate
k
[H2][ICI]?
O Rate
k [H2][ICI]²](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/6bf878e8-f234-4f66-a1d2-75bcef7aa11d/ad76b2aa-5128-4886-af02-ce3ecefbb041/phuqqbi_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:O Rate
k [HI][ICI]
Rate =
k [H2][ICI]² [HI]
O Rate
k [H2][ICI]
[HCI]²[I2]
Rate
k
[H2][ICI]?
O Rate
k [H2][ICI]²
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the mechanism. Step 1: Step 2: Overall: A B+C C+D E - equilibrium slow A+DB+E Determine the rate law for the overall reaction, where the overall rate constant is represented as k.arrow_forwardOne of the reactions that occurs in polluted air in urban areas is 2NO2(g) + O3(g) –→N2O5(g) + O2(g). Assume that a species with the formula NO3 is involved in the mechanism, and the observed rate law for the overall reaction is rate = k[NO2][O3]. Propose a mechanism for this reaction that includes the species NO3 and is consistent with the observed rate law. NO2(g) + O3(g) – NO3(g) + O2(g) (fast) NO3(g) + NO2(g) → N2O5(g) (slow) NO2(g) + O3(g) – NO3(g) + O2(g) (fast) 4NO3(g) 2N2O5(g) + O2(g) (slow) NO2(g) + O3(g) –→ NO3(g) + O2(g) (slow) NO3(g) + NO2(g) → N2O5(g) (fast) NO2(3) + O3(g) → NO3(g) + O2(g) (slow) 4NO3(3) → 2N20O5(g) + O2(g) (fast)arrow_forwardFor the following reaction Mechanism write the overall reaction and write the rate law. H3O++ I- → HI + H2O (fast) H2O2 + HI → H2O + HOI (fast) HOI + H3O++ I- →2H2O + I2 (slow) I2 + I- → I3-(fast)arrow_forward
- 1) NO(g) + O2 (g) >< NO3 (g) 2) NO3(g) + NO(g) > < 2NO2(g0 for the reaction mechanism given, what is the rate law for each elementary equation? What is the rate law for the overall reaction if the mechanism is correct?arrow_forward4. The rate law for the reaction H₂ (g) + I₂ (g) → 2 HI (g) was determined to be rate = k [H₂] [1₂], which led to a simple single-step bimolecular mechanism where an H₂ molecule simply collided with an I₂ molecule. In the 1960s, though, different teams found spectroscopic evidence for this mechanism: (1) (2) (3) I₂ (g) →21 (g) H₂(g) + I (g) → H₂I (g) H₂I (g) + I (g) → 2 HI (g) (fast) (fast) (slow) Show that this mechanism is consistent with the rate law: rate = k [H₂] [1₂]. To do this, assign individual rate constants for ALL forward and reverse reactions in the mechanism (I'm guessing k₁, k-1, k2, k-2 and k3). Then show that the overall rate law from combining individual rate laws for the mechanism steps yields rate = (some combination of k's) [H₂] [1₂], and thus k= (some combination of k's). Remember that there should be no reaction intermediates in the rate law, only reactants. \arrow_forwardA2 -> 2A (slow) 2A + B2 -> 2AB (fast) What is the rate law for the overall reaction?arrow_forward
- Consider the mechanism. O3 + NO, – NO, + O, NO, + NO, – N,O5 slow fast O, + 2 NO, – 0, + N,O5 Identify the rate law for the overall reaction based on the mechanism. rate = k[O,||NO,? rate = k[O3] rate = k[O3][NO,1 rate = k[NO,? k[NO, ][NO3] rate =arrow_forwardPlease make sure that the answer that I get is correct thank you so mucharrow_forwardThe rate law for the reaction: NH4+ + NO₂ N₂ + 2H₂O is rate =k[NH4+][NO₂] It is found that the rate constant for this reaction is 3.05x10-4 M-1s-1. Calculate the rate of the reaction, including units, if [NH4*] is 0.265M and [NO₂] is 0.0803M. Attach File Browse Local Filesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY