
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:For the 'Go-Back-N' protocol, which of the following statements about the receiver is FALSE?
The receiver uses a checksum to identify corrupted packets
None of the mentioned
The receiver needs to store all sequence numbers received since the beginning of the transmission
The receiver can generate duplicate ACKS
The receiver discards out of order packets
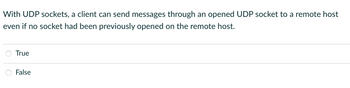
Transcribed Image Text:With UDP sockets, a client can send messages through an opened UDP socket to a remote host
even if no socket had been previously opened on the remote host.
True
False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider sending a file of F bits over a path of Q links. Each link transmits at R bits per second (bps). The network is lightly loaded so that there are no queueing delays. When a form of packet switching is used, the F bits are broken up into packets, each packet with L bits, of which h bits of it are header. Propagation delay is negligible. Let F = 5x104, Q = 20, R = 1 Mbps, L = 1000, and h = 10. c. Suppose the network is a packet-switched virtual circuit network. Denote the VC set-up time by ts = 250 milliseconds. How long does it take to send the file from source to destination?arrow_forwardConsider the GBN protocol with a sender window size of 4 and a sequence number range of 1,024. Suppose that at time t, the next in-order packet that the receiver is expecting has a sequence number of k. Assume that the medium does not reorder messages. Answer the following questions: a. What are the possible sets of sequence numbers inside the sender's window at time !? Justify your answer. b. What are all possible values of the ACK field in all possible messages currently propagating back to the sender at time? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardPlease give me correct solution.arrow_forward
- For each of following ICMP messages, list their possible senders (routers, non-destination hosts, and destination hosts). a) Type: destination unreachable,Code: 2/3 – protocol/port is unreachable b) Type: source quench,Code: 0 c) Type: time exceeded,Code: 1 (note when the final destination does not receive all of the fragments in a settime, it discards the received fragments and sends a time-exceeded message (code 1) tothe original source) d) Type: Redirection,Code: 1 – redirect to a host-specific routearrow_forwardThe ACK packets that pass from the recipient to the sender do not have sequence numbers in protocol rdt3.0, but they have an ACK area that includes the packet sequence number they are recognizing. Why does it not need sequence numbers for our ACK packets?arrow_forwardAll packets are treated equally in Priority Queuing. Select one: O True O Falsearrow_forward
- UDP and TCP use 1s complement for their checksums. Suppose the receive received two 3-bits payload messages: 010, 001. The checksum received is 100. Find all possible original messages. How many errors were made during the transmission?arrow_forwardHow many packets would the receiver have to be in order to make sure the acknowledgements have been sent and received until they can no longer receive them?arrow_forwardHow are the Standard Access List and the Extended Access List different from one another? How is the process of filtering packets carried out?arrow_forward
- The sender is aware of a constant round-trip delay between themselves and the recipient. Is a timer still needed in protocol rdt 3.0 considering the risk for packet loss? Explain.arrow_forwardAssume that there is a constant roundtrip delay between the sender and the recipient, and that the sender is aware of this delay. Is the use of a timer in protocol rdt 3.0 still required, given the possibility of packet loss? Explain.arrow_forwardAssume a sender sends 5 packets: 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4. The sender receives anACK with ackNo = 3. What is the interpretation if the system is using “Go-Back-N Protocol” or “Selective Repeat”? a. Go-Back-N Protocol b. Selective Repeatarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education