
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
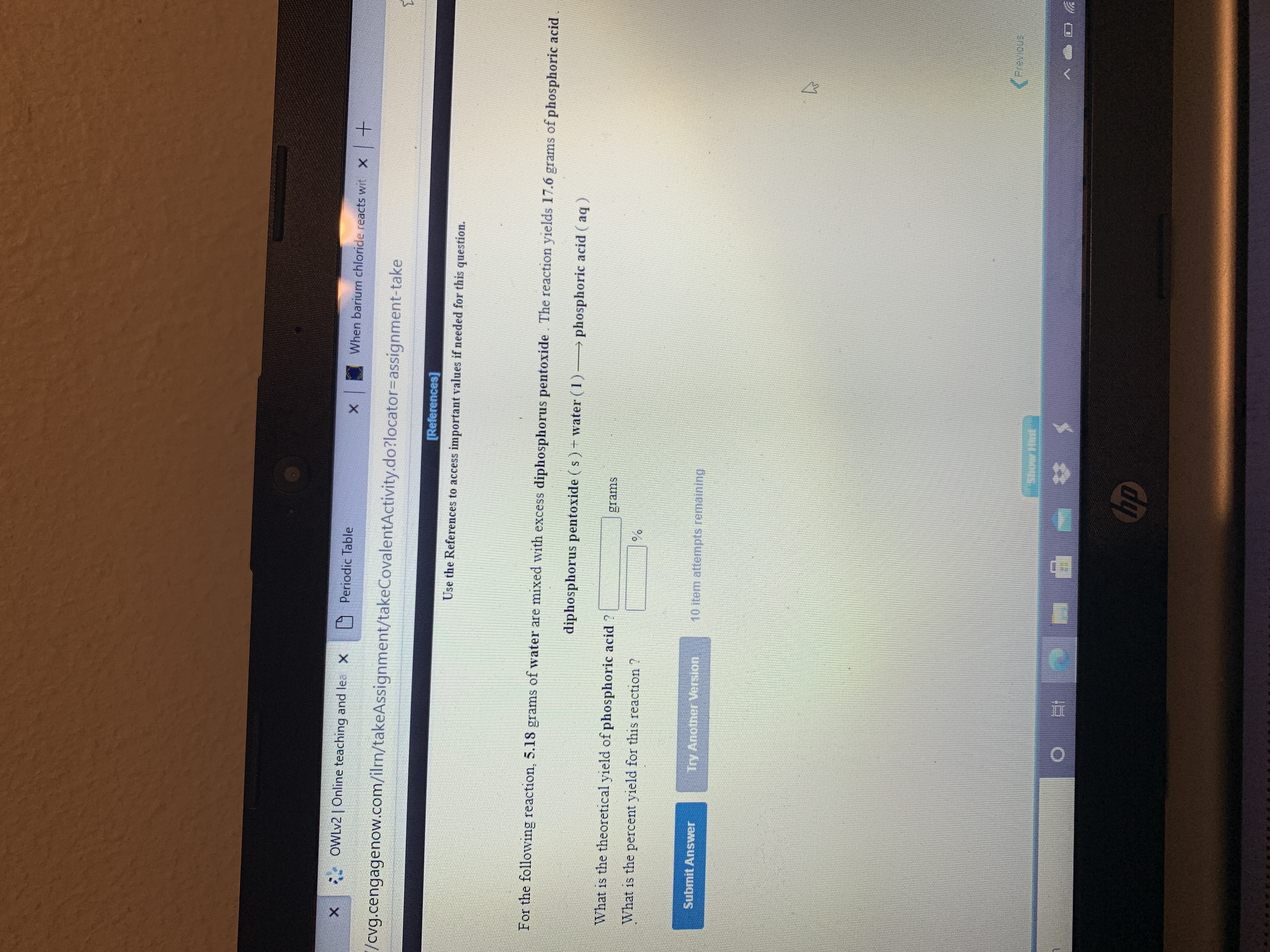
Transcribed Image Text:For the following reaction, 5.18 grams of water are mixed with excess diphosphorus pentoxide. The reaction yields 17.6 grams of phosphoric acid
diphosphorus pentoxide ( s)-water (1)-
→ phosphoric acid ( aq)
What is the theoretical yield of phosphoric acid ?
grams
What is the percent yield for this reaction ?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each of the following unbalanced equations, calculate how many grams of each product would be produced by complete reaction of g of the reactant indicated in boldface. Indicate clearly the mole ratio used for the conversion. TiBr₄(g)+H₂(g)→Ti(s)+HBr(g) SiH₄(g)+NH₃(g)→Si₃N₄(s)+H₂(g) NO(g)+H₂(g)→N₂(g)+2H₂O(℩) Cu₂S(s)→Cu(s)+S(g)arrow_forwardFor the reaction shown, calculate how many grams of each product form when the following amounts of reactant completely react to form products. Assume that there is more than enough of the other reactant. 2Al(s)+Fe2O3(s)→Al2O3(s)+2Fe(l) -Calculate the mass of Al2O3 formed when 4.1 gAl completely react.Express your answer using two significant figures. -Calculate the mass of Fe formed when 4.1 gAl completely react. -Calculate the mass of Al2O3 formed when 4.1 gFe2O3 completely react.Express your answer using two significant figures. -Calculate the mass of Fe formed when 4.1 gFe2O3 completely react.Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 6.70 grams of diphosphorus pentoxide are mixed with excess water. The reaction yields 6.34 grams of phosphoric acid. diphosphorus pentoxide (s) + water (1)→phosphoric acid (aq) What is the theoretical yield of phosphoric acid What is the percent yield for this reaction? grams %arrow_forward
- If a solution containing 54.2154.21 g of lead(II) chlorate is allowed to react completely with a solution containing 8.5648.564 g of sodium sulfide, how many grams of solid precipitate will be formed? mass of solid precipitate: gg How many grams of the reactant in excess will remain after the reaction? mass of excess reactant: gg Assuming complete precipitation, how many moles of each ion remain in solution? If an ion is no longer in solution, enter a zero (0) for the number of moles. Pb2+=Pb2+= molmol ClO–3=ClO3–= molmol Na+=Na+= molmol S2−S2− molarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 0.557 moles of potassium hydroxide are mixed with 0.224 moles of phosphoric acid. potassium hydroxide(aq)+phosphoric acid(aq)= potassium phosphate(aq)+water(l) What is the formula for the limiting reagent? What is the maximum amount of potassium phosphate that can be produced?arrow_forwardAccording to the following reaction, how many moles of potassium sulfate will be formed upon the complete reaction of 24.0 grams of potassium hydrogen sulfate with excess potassium hydroxide?potassium hydrogen sulfate (aq) + potassium hydroxide (aq) potassium sulfate (aq) + water (l)? moles potassium sulfatearrow_forward
- According to the following reaction, how many grams of ammonia will be formed upon the complete reaction of 23.1 grams of hydrogen gas with excess nitrogen gas?nitrogen (g) + hydrogen (g) ammonia (g)arrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 10.6 grams of sodium are allowed to react with 5.70 grams of water .sodium ( s ) + water ( l ) sodium hydroxide ( aq ) + hydrogen ( g )What is the maximum amount of sodium hydroxide that can be formed? grams What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? gramsarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 9.90 grams of benzene (C,Hg) are allowed to react with 15.2 grams of oxygen gas. benzene (C,H6) (1) + oxygen (g)- →carbon dioxide (g) + water (g) What is the maximum amount of carbon dioxide that can be formed? | grams What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? | gramsarrow_forward
- For the following reaction, 58.6 grams of potassium hydroxide are allowed to react with 37.9 grams of phosphoric acid potassium hydroxide ( aq ) + phosphoric acid ( aq ) potassium phosphate ( aq ) + water ( I ) What is the maximum amount of potassium phosphate that can be formed? grams What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? grams Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item altempts remainingarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 28.3 grams of calcium hydroxide are allowed to react with 24.4 grams of hydrochloric acid calcium hydroxide(aq) + hydrochloric acid(aq)- → calcium chloride(aq) + water(1) What is the maximum amount of calcium chloride that can be formed? grams What is the FORMIULA for the limiting reagent? What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? gramsarrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 5.68 grams of chlorine gas are mixed with excess phosphorus (P4) . The reaction yields 5.34 grams of phosphorus trichloride .phosphorus (P4) ( s ) + chlorine ( g ) phosphorus trichloride ( l ) What is the theoretical yield of phosphorus trichloride ? grams What is the percent yield for this reaction ? %arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY