
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
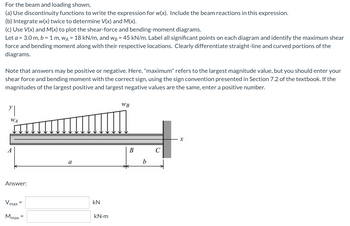
Transcribed Image Text:For
the beam and loading shown,
(a) Use discontinuity functions to write the expression for w(x). Include the beam reactions in this expression.
(b) Integrate w(x) twice to determine V(x) and M(x).
(c) Use V(x) and M(x) to plot the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams.
Let a = 3.0 m, b = 1 m, WA = 18 kN/m, and wg = 45 kN/m. Label all significant points on each diagram and identify the maximum shear
force and bending moment along with their respective locations. Clearly differentiate straight-line and curved portions of the
diagrams.
Note that answers may be positive or negative. Here, "maximum" refers to the largest magnitude value, but you should enter your
shear force and bending moment with the correct sign, using the sign convention presented in Section 7.2 of the textbook. If the
magnitudes of the largest positive and largest negative values are the same, enter a positive number.
WB
"|
WA
X
C
a
Answer:
Vmax
Mmax
KN
kN.m
B
b
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the beam and loading shown,(a) Use discontinuity functions to write the expression for w(x). Include the beam reactions in this expression.(b) Integrate w(x) twice to determine V(x) and M(x).(c) Use V(x) and M(x) to plot the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams.Let a = 3.8 m, b = 1.3 m, wA = 17 kN/m, and wB = 51 kN/m. Label all significant points on each diagram and identify the maximum shear force and bending moment along with their respective locations. Clearly differentiate straight-line and curved portions of the diagrams.Note that answers may be positive or negative. Here, "maximum" refers to the largest magnitude value, but you should enter your shear force and bending moment with the correct sign, using the sign convention presented in Section 7.2 of the textbook. If the magnitudes of the largest positive and largest negative values are the same, enter a positive number.arrow_forwardCan you help with this question? Thank you!arrow_forwardA 240mm diameter circular simply supported beam carries a concentrated load, uniformly distributed load and a triangular load as shown in the figure. Using Area Moment Method, Solve the following unknowns. Let P = 195KN, a = 2m, and the modulus of elasticity of beam is 100GPA. NOTE: WRONG SIGN IS WRONG. WRONG UNITS IS WRONG. w w B Im If the shear at a point 1m from the roller support is equal to -182.66666666667KN, determine the value of "w". kN/m Determine the deflection at point 2n from the hinge support. (Note: Put a negative sign if the deflection is going down) IIIarrow_forward
- Using the stiffness method - direct formulation: (1) develop the equations equilibrium ([K] {D} = {Q} in matrix form (matrix [K] 2x2), E = 200GPa and I=200 x106 mm4arrow_forwardSOLVE STEP BY STEP The simple portico in the figure consists of a rigid lintel of length L supported by two cylindrical pillars of equal length and material. A triangular distributed load of maximum value q_0 is imposed on the lintel. Calculate the ratio between the cross sections of the columns so that buckling starts in both at the same time. Ignore the shortening of the pillars do 1 2arrow_forwardA beam is subjected to a bending moment, as shown in the figure below, where point B is assumed to be an internal connection, point C is assumed to be a rolling bearing, and the flexural stiffness of the beam section is a constant EI:(a) Use the Conjugate Beam Method to find the slope of point B after deformation.(b) Same as above, try to find the vertical displacement of point D.Tip: The left and right slopes of point B may be differentarrow_forward
- Solve the problem by the moment-area method. The beam has constant flexural rigidity EI. A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P at the positions shown in the figure. B C 4. 4 A support C at the midpoint of the beam is positioned at distance d below the beam before the loads are applied. Assuming that d = 12 mm, L = 5.4 m, E = 200 GPa, and I = 193 x 10° mm, calculate the magnitude of the loads P (in kN) so that the beam just touches the support at C. 163.87 x kNarrow_forwardFor the simply supported beam subjected to the loading shown, derive equations for the shear force V and the bending moment M for any location in the beam. (Place the origin at point A.) Let a=1.50 m, b=5.00 m, PA = 75kN, and PC = 90kN. Construct the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams. Calculate the reaction forces By and Dy acting on the beam. Positive values for the reactions are indicated by the directions of the red arrows shown on the free-body diagram below.arrow_forwardsimply supported beam is subjected to a uniform load of 400 lb/ft and a concentrated load of 900 lb as shown in the below figure a. Find the reactions. b. Express the internal shear and moment in terms of x and then draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam. Label the points of maximum bending on the bending moment diagram. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses due to bending and specify their location. 900 lb =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning