
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
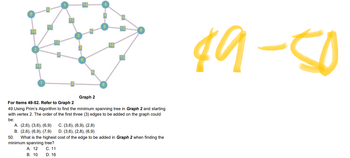
Transcribed Image Text:### Graph 2 - Educational Content
#### For Items 49-52. Refer to Graph 2
49. **Using Prim’s Algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree in Graph 2 and starting with vertex 2.** The order of the first three (3) edges to be added on the graph could be:
- **A.** (2,6), (3,6), (6,9)
- **B.** (2,6), (6,9), (7,9)
- **C.** (3,6), (6,9), (2,8)
- **D.** (3,6), (2,8), (6,9)
50. **What is the highest cost of the edge to be added in Graph 2 when finding the minimum spanning tree?**
- **A.** 12
- **B.** 10
- **C.** 11
- **D.** 16
#### Explanation of the Graph:
The graph displayed is a connected, undirected graph comprising nodes labeled from 1 to 16. The edges between these nodes are represented with numerical weights, signifying the cost or distance between connected nodes. Notably, some of the vertices include:
- Vertex 1 connects to vertices 2 (weight 1) and 4 (weight 3), and other vertices with different weights.
- Vertex 2 is connected primarily to vertices such as 6 (weight 3) and 9.
- Vertex 8 connects to vertices including 5 (weight 12) and 10.
To solve the questions using Prim’s Algorithm, start with the specified vertex (in this case, vertex 2) and sequentially add the minimum weighted edge that connects a new vertex to the growing spanning tree until all vertices are connected with the minimum possible total weight.
For further visual understanding, students can trace the algorithm on the provided graph image, identifying the edges and their respective weights as they work through the given options.
Prim’s Algorithm for reference:
1. Initialize the spanning tree with a single vertex (chosen arbitrarily).
2. Find the edge with the smallest weight that expands the growing spanning tree by adding a vertex not already in the tree.
3. Repeat step 2 until all vertices are included in the spanning tree.
These concepts are foundational for understanding graph theory applications in computer science and network design.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Help me please: Consider the graph in Figure 20-20. Find the shortest distance from node 0 to every other node in the graph.arrow_forwardConstruct the simple graph of 4 vertices, where degree(v1)=3,degree(v2)=2,degree(v3)=2,degree(v4)=1 What is the total number of edges of the complete simple graph of 4 vertices Write a formula to find the total number of edges in a complete simple graph based on n where n is the total number of vertices. How many adjacent vertices to a vertix of degree 3arrow_forward2. Consider the graph G2(V2, E2) below. 2a. Find the MST of this graph with Kruskal’s algorithm. Draw the MST, and show the table [edge] [w(u, v)] [mark]. 2b. Find the MST of this graph with Prim’s algorithm starting at vertex 'a'. Draw the MST and list the vertices in order you added them to the MST. 2c. Would you get a different MST if you repeat 2b starting at vertex 'e'? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- Given the following graph, A C 3 1 E 4 В F 7 D 5 What is the next edge and vertex(s) to be included in the solution if a. we are using Prim's algorithm to find a minimum spanning tree and we have started with vertex E? Edge: Vertex(s): What is the next edge and vertex(s) to be included in the solution if b. we are using Kruskal's algorithm to find a minimum spanning tree Edge: Vertex(s): What is the next edge and vertex(s) to be included in the solution if c. we are using Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm to find shortest paths and we have started with vertex E, with C and F already included in the shortest path tree? Edge: Vertex(s):arrow_forwardMark Zuckerberg, the CEO of Facebook, has hired you to lead the Facebook Algorithms Group. He has asked you to use various graph algorithms to analyze the world's largest social network. The Facebook Graph has 2.8 billion vertices, with each vertex being a Facebook user. Two vertices are connected provided those two users are "friends". The first decision you need to make is how you want to model the Facebook graph. Determine whether you should use an adjacency-list representation or an adjacency-matrix representation.arrow_forwardWith a given graph below, run the Bellman-Ford Algorithm to find the shortest path from node s to all nodes. For example, (0, 100, 23, 300, 50) for (node 1, node 2, node 3, node 4, node 5)arrow_forward
- 1. Use the graph below to answer the following questions. A B H 10 G 10 25 20 5 50 5 5 30 5 15 C 20 D F 15 E (a) Use Kruskal's Algorithm to produce a minimum spanning tree. Write down the edges that you choose in order of the algorithm. (b) Use Prim's Algorithm to produce a minimum spanning tree (assume A is the root/source). Write down the edges that you choose in order of the algorithm.arrow_forwardUsing the Kruskal’s Algorithm, show the minimum spanning tree representation of the graph.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education