
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
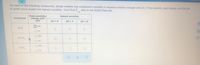
Transcribed Image Text:For each of the following compounds, decide whether the compound's solubility in aqueous solution changes with pH. If the solubility does change, pick the pH
at which you'd expect the highest solubility. You'll find K
data in the ALEKS Data tab.
sp
Does solubility
change with
pH?
highest solubility
compound
pH = 8
pH = 7
pH = 6
O yes
KCI
O no
O yes
CaCO,
O no
O yes
Ca Cl,
O no
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following aqueous solutions are good buffer systems? O 0.34 M ammonium nitrate + 0.31 M ammonia O 0.20 M sodium hydroxide + 0.23 M sodium chloride O 0.37 M hydrofluoric acid + 0.25 M sodium fluoride O 0.17 M nitrous acid + 0.11 M sodium nitrite O 0.21 M perchloric acid + 0.17 M sodium perchloratearrow_forwardKSP for Copper Sulfide is: 7.9 × 10-37 KSP for Copper Hydroxide is: 1.6 × 10-19arrow_forwardChemistry Determine the pH of a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. NEXT > The buffer was prepared by dissolving 20.0 g NaCH,CO0 into a 500.0 mL solution of 0.150 M of CH,COOH. Assume the volume of the solution does not change. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products. CH,COOH(aq) + H,O(1) H,O"(aq) + CH,COO (aq) Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) 5 RESET 20.0 0.150 0.244 0.488 0.678 20.0+ 20.0- 0150 +1 0.150- 0.244+ 0.488 0.244- 0.488-x 0678 0.678-1 Determine the pH of a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. NEXT ( PREV The Ka for CH,COOH, is 1.8 x 10, Based on your ICE table (Part 1) and the…arrow_forward
- The initial in the unknown analysis is the addition of 6. M HCl. This results in the formation of a precipitate. The solid precipitate is separate from the liquid solution. The solution could potentially contain K+, Ca2+, and Al3+. Next, 3M NH3 is added to the solution to separate the Al3+. This is a result of the fact that the Al3+ forms the hydroxide, Al(OH)3. But Ca2+ also forms the hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Why does the Ca(OH)2 not separate out with the Al(OH)3?arrow_forwardWhich of the following aqueous solutions are good buffer systems? O 0.36 M hydrofluoric acid + 0.23 M potassium fluoride O 0.27 M hydrochloric acid + 0.22 M sodium chloride O 0.15 M potassium hydroxide + 0.24 M potassium chloride O 0.15 M hydrocyanic acid + 0.15 M sodium cyanide O 0.27 M ammonium bromide + 0.33 M ammoniaarrow_forwardCalculate the solubility at 25 °C of Ni(OH)2 in pure water and in a 0.0170M NaOH solution. You'll find K sp Round both of your answers to 2 significant digits. solubility in pure water: solubility in 0.0170 M NaOH solution: 0- 00 x10 X ☐☐ 5 010 data in the ALEKS Data tab.arrow_forward
- Complete the following solubility constant expression for PbCrO 4. K sp = 0 X Śarrow_forwardComplete the following solubility constant expression for BaSO4. K sp = 0 X 90 010 5arrow_forwardDetermine the pH of a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. The Ka for CH COOH is 1.8 x 10%. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. 2 3 NEXT > The buffer was prepared by dissolving 20.0 g NaCH,COO into a 500.0 mL solution of 0.150 M of CH COOH. Assume the volume of the solution does not change. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products. Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) CH COOH(aq) H₁₂O(I) HO*(aq) CH COO(aq)arrow_forward
- Which of the following aqueous solutions are good buffer systems? 0.30 M ammonia + 0.34 M potassium hydroxide 0.20 M hydrochloric acid + 0.20 M sodium chloride 0.15 M sodium hydroxide + 0.24 M sodium chloride 0.21 M hydrocyanic acid + 0.15 M sodium cyanide 0.39 M sodium nitrate + 0.28 M potassium nitratearrow_forwardDetermine the pH of a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. The Ka for HC,H₂O₂ is 6.3 × 105. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. > The buffer was prepared by dissolving 21.5 g HC,H₂O₂ and 37.7 g of NaC,H₂O₂ in 200.0 mL of solution. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products. Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) 0.178 0.880 - x 1 HC,H,O,(aq) 0 0.888 1.31 + x 21.5 +x 0.178 + x + 37.7 -X 2 H₂O(1) 0.888 + x 0.176 21.5-x = 0.261 3 H,O*(aq) 37.7 + x 0.880 0.176-x + RESET 1.31 C,H,O,(aq) NEXT 0.261 + x Determine the pH of a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. The Ka for HC₂H₂O₂ is 6.3 × 10¹5. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. PREV [0] [0.888] [1.31 + x] 1 Based on your ICE…arrow_forwardYou want to determine the concentration of chloride in a water sample. You were to add appropriate amount of AgNO 3 to 2.000 L of the water sample and collect a precipitate with a mass of 1.3591 g. The molecular mass AgNO 3 is 169.87 g/mol. The molecular mass of AgCl is 143.32 g/mol. The K sp of AgCl is 1.7x10-10 . What is the concentration of chloride in the water sample?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY