
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
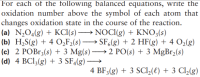
Transcribed Image Text:For each of the following balanced equations, write the
oxidation number above the symbol of each atom that
changes oxidation state in the course of the reaction.
(a) N,O4(g) + KCI(s) → NOCI(g) + KNO3(s)
(b) H,S(g) + 4 O̟F2(s) –
(c) 2 POB13(s) + 3 Mg(s) → 2 PO(s) + 3 MgBr2(s)
(d) 4 BCI3(g) + 3 SF4(g) ·
→ SF,(g) + 2 HF(g) + 4 O2(g)
4 BF3(g) + 3 SCI2(t) + 3 Cl2(g)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 15 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider the following precipitation reaction: 5 Fe2+(aq) + MnO4-(aq) + 8 H+(aq) → 5 Fe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l) An iron sample weighing 0.276 g is converted into Fe2+(aq) and requires 31.57 mL of MnO4-(aq) according to the equation above. What is the Molarity of the MnO4-(aq) solution?arrow_forwardConsider the chemistry that occurs when 150.0 mL of 0.150 M Pb(NO3)2 (aq) and 150.0 mL of 0.250 M KCI (aq) are combined. (a) Write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs. (b) Determine the mass of the insoluble product formed. (c) Determine the molar concentration of the ion that is in excess. (You do not need to calculate the concentration of any spectator ions.)arrow_forwardThe following reaction is a precipitation reaction. NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → NaNO3 (aq) + AgCl (s) a metal displacement a decomposition an acid-base neutralizationarrow_forward
- 3. Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any). that occurs when aqueous solutions of K2S and Fe(NO;)2 are mixed. A) K*(aq) + NO;(aq) – KNO;(s) B) No reaction occurs. C) Fe"(aq) + S³(aq) + 2 K^(aq) + 2 NO;(aq) → FeS(s) + 2 K“(aq) +2 NO;(aq) D) Fe"(aq) + S²(aq) + 2 K*(aq) + 2 NO;(aq) → Fe²"(aq) + s²(aq) + 2 KNO3(s) E) Fe2(aq) + S²-(aq) FeS(s)arrow_forwardApply the concepts of stoichiometry and solution concentration in this section. Potassium iodide reacts with lead (II) nitrate in the following precipitation reaction 2 KI (aq) + Pb(NO3)2 (aq) KNO3 (aq) + PbI2 (s). What volume of 0.200 M KI solution is required to completely precipitate all of the lead in 255mL of a 0.312 M Pb(NO3)2 solution? An solution is made by dissolving 28.4 g of glucose (C6H12O6) in 355 g of water. The final volume of the solution is 378 mL. Calculate the molarity, molality, mole fraction, mole percent and mass percent of the solution, Hydrochloric acid is usually purchased in a concentrated form that is 37.0 % HCl by mass and has a density of 1.20 g/mL. Describe exactly how to prepare 2.85 L of a 0.500 M HCl to be used in Dr. Henary’s CHEM1211K lab from the concentrated solution. Hint (Find molarity of concentrated solution and use dilution equation. This is how your solution are prepared)arrow_forwardWhich of the following reactions will produce a precipitate? Na₂SO4 (aq) + CuCl₂ (aq) → KF (aq) + AgNO3(aq) → Li₂CO3 (aq) + Mg(C₂H3O2)2 (aq) → Fe₂(SO4)3 (aq) + NH4ClO3 (aq) → AlCl3 (aq) + K3PO4 (aq) → Ba(ClO4)2 (aq) + (NH4)2S (aq) →arrow_forward
- Calculate the molarity of the following solutions: (a) 0.14 mol of solute in 79.2 mL of solution (b) 2.99 mol of KBr in 0.46 L of solution (c) 27.5 g of NaC2H3O2 in 1.67 L of solution (d) 80 . g of CuSO4 · 5H2O in 8.5 L of solutionarrow_forwardA chemist performs a gravimetric analysis. The chemist combines 1.00 L of 2.00 M AGNO, (ag) with 1.00 L of 4.00M NaCl (ag) in an Erlenmeyer flask. Both the AgNO3 (aq) solution and the NaCl(aq) solution are colorless. After the mixture has been stirred, a cloudy white substance is observed at the bottom of the flask. What is the expected mass of AgCl (s), in grams, assuming that the yield is 100%? In the box, enter the mass to the nearest gram.arrow_forwardCalculate the molarity of the following solutions: (a) 0.85 mol of solute in 135 mL of solution (c) 260. g of C6H12O6 in 632 mL of solution (d) 128. g of MgSO4 · 7 H2O in 4.75 L of solutionarrow_forward
- 2. The solubility of KClO, at several temperatures is shown in the accompanying diagram. Solubility, g per 100 g H₂O 50 40 30 20 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Temperature, °C If a student mixes 10.0 g of KCIO, with 45.0 g of H₂O at 70 ° C. Which statement about the final solution is correct? (A) It is a saturated solution. (B) It is a supersaturated solution. (C) It is an unsaturated solution. (D) It is impossible to determine.arrow_forwardFor each of the following reactions, suggest two soluble ionic compounds that, when mixed together in water, result in the net ionic equation given: (a) 2 Ag+ (aq) + CO3²¯ (aq) → Ag₂CO3(s) (b) Mg²+ (aq) + 2 OH¯(aq) → Mg(OH)₂(s), the suspension present in milk of magnesia 3+ (c) 3 Ca³+ (aq) + 2 PO2 (aq) → Ca3(PO4)2(s), gypsum, a component of concretearrow_forwardThe following equation represents the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and magnesium acetate are combined. Mg(CH3COO)2(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) Mg(OH)2(s) + 2NaCH3COO(aq) Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction. Assume that all ionic compounds that are in aqueous solution are dissociated. Use the pull-down choices to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed leave it blank. ______ + ______ + ______ + ______ >>> ______ + ______arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY