
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
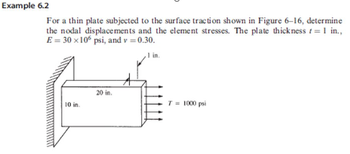
Transcribed Image Text:Example 6.2
For a thin plate subjected to the surface traction shown in Figure 6-16, determine
the nodal displacements and the element stresses. The plate thickness f = 1 in.,
E = 30 x 106 psi, and v = 0.30.
,1 in.
10 in.
20 in.
A
T = 1000 psi
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please give me right solution a,b and c...arrow_forwardConsider a point in a structural member that is subjected to plane stress. Normal and shear stress magnitudes acting on horizontal and vertical planes at the point are Sx = 46 MPa, Sy = 61 MPa, and Sxy = 14 MPa. (a) Determine the principal stresses and the maximum in-plane shear stress acting at the point. (b) Show these stresses on an appropriate sketch (e.g., see Figure 12.15 or Figure 12.16) (c) Compute the absolute shear stress at the point.arrow_forwardC. A rigid steel bar is suspended horizontally by 1m steel rod at one end and 2m bronze rod at the other end as shown. Neglecting the mass of the steel bar, at what distance X (in meters) from the steel rod should a 20 kN force be placed so that the steel bar will remain horizontal? Also, calculate the stresses in steel and bronze rod (in MPa). Use the following data. Steel, st Bronze, Br Br. 2m 20000 N Area (mm²) 600 300 St. 1m -X- E(GPa) 200 83 10 marrow_forward
- Consider a point in a structural member that is subjected to plane stress. Normal and shear stress magnitudes acting on horizontal and vertical planes at the point are S, = 8.0 ksi, S, = 10.5 ksi, and Sxy = 8.0 ksi. (a) Determine the principal stresses and the maximum in-plane shear stress acting at the point. (b) Show these stresses on an appropriate sketch (e.g., see Figure 12.15 or Figure 12.16) (c) Compute the absolute shear stress at the point. Sy Sxy S.arrow_forwardThe rectangular plate is subjected to force P that causes elongation in the horizontal direction and shrinking in the vertical direction as shown with the dashed line in the figure. Assume a = 550 mm, Δx = 2 mm, and Δy = 1.1 mm. Determine the shear strain γxy at point A?in micro rad Determine the shear strain γnt at point A?in micro rad What is the normal strain in the x-direction?micro£arrow_forwardDue to loading, the plate is deformed into the dashed shape shown in the figure. Assume a = 39 in., b= 33 in., δ1= 0.1625 in., δ2= 0.1 in. Determine the average normal strain along the side AB?in micro rad And answer in right and clear way Determine the average shear strain in the plate at A relative to the horizontal and vertical axes?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning