
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
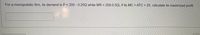
Transcribed Image Text:For a monopolistic firm, its demand is P 200 - 0.25Q while MR = 200-0.5Q, if its MC = ATC = 20, calculate its maximized profit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The accompanying graph depicts average total cost (ATC) marginal cost (MC), marginal revenue (M), and demand (D) 50 facing a monopolistically competitive firm MC 45 Place point A at the firm's profit maximizing price and quantity 40 35 What is the firm's total cost? ATC 30 25 total cost: 20 15 What is the firm's total revenue? 10 5 total revenue: $ MR 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95100 Quantity What is the firm's total profit? profit: $ Price and Cost ($)arrow_forwardA small, local restaurant in St. Augustine, FL, serves scrambled eggs for breakfast. The market for breakfast scrambled eggs is monopolistically competitive. The following graph shows the demand, MR, MC, and ATC curve of this local restaurant. Use the graph to answer questions 3 to 7. Price (P) per plate $10 7 5 3 2 0 MC MR 50 80 100 ATC Number of plates of scrambled eggs served per day (Q)arrow_forwardSuppose the graph represent demand and marginal cost for a firm that is able to engage in perfect price discrimination. What is this firm's profit? Price and costs $50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 D 0 10 20 30 40 50 MC = ATC T 60 70 80 90 100 Downloads per hourarrow_forward
- A perfectly competitive firm is expected to make a $0 economic profit in the long-run. What type(s) of profit would you expect a monopolist to earn in the long-run? Why the difference? Use the editor to format your answerarrow_forwardThe graph below shows cost and revenue curves for a monopolistic competitor producing different amounts of chairs. On the graph, suppose that: A = $55, B = $21, C = $15, E = $7, F = 13, and G = 31 Price BL BCE CP MC ATC EH MR F G Quantity Calculate the maximum profit the firm can earnarrow_forwardif a monopolistic firm takes over a perfectly competaive market we would expect to see market price of the goof to fall because demand is perfectly eleastic rise and quantity is sold fall as the monopolist tries to increase sales rise and the quantity sold to increasearrow_forward
- What does it mean in a monopolistically competitive market, when the rule for maximizing profit is to set MR = MC? Group of answer choices Price is equal to marginal revenue. Price is equal to marginal cost. Price is lower than marginal revenue. Price is higher than marginal revenue.arrow_forwardA large corporation with monopolistic control in the marketplace has its average daily costs, in dollars, given by C = 500 x + 200x + x2. The daily demand for x units of its product is given by p = 450,000 − 100x dollars. Find the quantity that gives maximum profit.x = unitsarrow_forwardexplain the relationship between the market price and a monopolistically competitive firm’s marginal revenue, be able to find the profit-maximizing output and pricearrow_forward
- What does it mean in a monopolistically competitive market, when the rule for maximizing profit is to set MR = MC? Group of answer choices Price is equal to marginal revenue. Price is equal to marginal cost. Price is lower than marginal revenue. Price is higher than marginal revenue.arrow_forwardIf this monopolistic firm's marginal cost is constant at $30, its profit maximizing output is: (Hint: Demand is linear (P-a-bQ) implying that the MR curve's slope is twice the demand curve slope; find the demand curve and then the MR curve.) Price $70 $50 $30 $10 10 20 30 40 50 units. 40 units. 20 units. 30 units. Demand 50 60 70 Quantityarrow_forwardDoes the monopolistic firm make a profit, loss, or zero economic profit in the long run?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education