
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
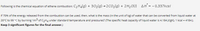
Transcribed Image Text:Following is the chemical equation of ethene combustion: C2 H4(g) + 302(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2 H20(1) AH = - 0.337kcal
If 70% of the energy released from the combustion can be used, then, what is the mass (in the unit of kg) of water that can be converted from liquid water at
20°C to 99 °C by burning 1m3 of C2H4 under standard temperature and pressures? (The specific heat capacity of liquid water is 4.184 J/(gK), 1 kcal = 4184 J.
Keep 3 significant figures for the final answer.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The oxidation of glucose, C6H12O6(s), is described by the following thermochemical equation:C6H12O6(s) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) ΔH = -2772 kJHow much heat, in kilojoules, can be produced by the oxidation of 3.56 g of fuel C6H12O6?Molar mass of C6H12O6 = 180.156 g/molarrow_forwardPart B 2.0000 g of the unknown compound is burned in a bomb calorimeter. During the combustion, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 23.125°C to 28.997 °C. During calibration, the heat capacity of the calorimeter was found to be 9.9897kJ °C-1. In the previous experiment, the molar mass of the substance was found to be 148.16 gmol-1. What is AcombU for the unknown compound? να ΑΣφ ? kJ mol1 Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardGiven: 4AICI3(s) + 302(g) → 2Al,O3(s) + 6C12(g); AH=-529.0 kJ determine AH for the following thermochemical equation. Cl,(3) + Al,O;(s) → AICI,(9) + 02(g) O +88.2 kJ O +264.5 kJ O +176.3 kJ O -176.3 kJ O +529.0 kJarrow_forward
- To study the possible amount of energy generated by a person, the person can be roughly viewed as a constant pressure calorimeter using table sugar (sucrose, C12H22O11) as the energy generator. The reaction of table sugar in a calorimeter is given by: C12H22O11(s) + 12O2(g) ----------> 12CO2(g) + 11H2O(g) a. What is the heat released by consuming one mole of sugar (C12H22O11) in this way? b. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion per mole of sugar utilization. c. Does the result of your calculation make sense?arrow_forwardA piece of metal of mass 15 g at 99◦C is placed in a calorimeter containing 41.3 g of water at 19◦C. The final temperature of the mixture is 40.2◦C. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal? Assume that there is no energy lost to the surroundings. Answer in units ofJg·◦C.arrow_forwardThe table provides molar heat capacities (Cm) of selected metals with the units of joules per mole-kelvin. Heat capacity is also frequently given as specific heat capacity (C₂) with the units joules per gram-degree Celsius. Using the values provided in the table, convert the molar heat capacity (Cm) of zinc to the specific heat capacity (C₂) of zinc. C₁ = J/(g. °C) Molar heat capacity (Cm) of selected metals at 25 °C Element aluminum copper iron lead magnesium nickel titanium zinc Cm (J/(mol-K)) 24.20 24.44 25.10 26.84 24.87 26.07 25.06 25.39arrow_forward
- The molar heat capacity at constant pressure of carbon dioxide is 29.14 J/K.mol. (a) What is the value of its molar heat capacity at constant volume? _______ J/K/mol. 4 sig. number (b) Calculate the change in enthalpy when 1 mole carbon dioxide is heated from 15°C (the temperature when the air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs)? _______ J/mol. 4 sig. number normal format. (c) Calculate molar internal energy when carbon dioxide is heated from 19.58 °C (the temperature when the air is inhaled) to 37°C (blood temperature, the temperature in our lungs). ______ J/mol. 3 sig. number normal format.arrow_forwardAt constant volume, the heat of combustion of a particular compound is -3916.0 kJ/mol. When 1.329 g of this compound (molar mass = 166.62 g/mol) was burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter, including its contents, rose by 7.549 "C. What is the heat capacity (calorimeter constant) of the calorimeter? calorimeter constant: kJ/ "Carrow_forwardFructose, C6H12O6(s), is a sugar closely related to glucose.. A 0.755 g sample of fructose was combusted with excess oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, containing 500.0 g of water. The heat capacity of the empty calorimeter was 208 J/K. The temperature of the calorimeter and the water rose from 22.00°C to 27.12°C due to the combustion reaction, which formed CO2(g) and liquid water. What is the energy change, AU (in kJ), for the combustion of one mole of fructose under these conditions? -15600 -2810 +520 +254 -804arrow_forward
- How many grams of CaO must be added to 50.0 mL of water to make the temperature increase from 25.0 °C to 58.87 °C? The reaction is CaO(s) + H 2O(l) ↔ Ca(OH) 2(aq) -- ΔH = -83.7 kJAssume the heat capacity of the solution is the same as pure water (4.184 J/g*°C), the density of the solution is 1.00 g/mL and there is no loss of heat to the surroundings.arrow_forwardGasoline is composed primarily of hydrocarbons, includingmany with eight carbon atoms, called octanes. One ofthe cleanest–burning octanes is a compound called 2,3,4-trimethylpentane, which has the following structural formula: The complete combustion of one mole of this compoundto CO21g2 and H2O1g2 leads to ΔH° = -5064.9 kJ.(a) Write a balanced equation for the combustion of1 mol of C8H181l2. (b) By using the information inthis problem and data in Table 5.3, calculate ΔHf° for2,3,4-trimethylpentane.arrow_forward(1)Consider the reaction: 2A (g) + 3 B (g) → 2 C (g) ΔHrxn = +254.3 kJ What will be the enthalpy change (in kJ) if 0.471 mol B reacts in excess A? (2)Consider the reaction: C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ΔHrxn = -393.5 kJ What mass of carbon (in g) must be reacted via this mechanism to release 581.2 kJ of heat?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY