
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Can please solve question 4 and 5 explaining step by step on a picture please, thanks.
all the information it's on the first picture. where Uk= 1/2K((x2)^2-(x1)^2)) and Ug= mg(x2-x1) and K is the slope and in this case is 7.99 N/m. I think this is enough information to solve this thank you.
Just post the picute of all the step you did to solve it.
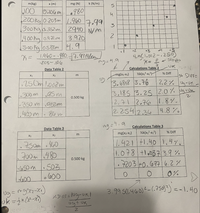
Transcribed Image Text:m(kg)
x (m)
mg (N)
k (N/m)
100 0.106 m
200kgl0.203m 1.960 7.99
300kgb.352m
980
2940 N/M
3.920
400 hg 0421m
500 kglosBm 4.9
1.960--980-7. 99N/
•3
X=
4,9(1.002-.250)
Slo pe
•203-106
mg-4.9
%3D
Data Table 2
Calculations Table 2
X1
mg(x2-X1)
¼k(x;²-x1?)
X2
% Diff
250m 1.002m
% Diffs
2.2% g-UR
3.6848 3,76
3.185 3.25 2.0% gtUk
2.71 2.76 1.8%.
2.2542.36 4.8%
.300m
a5 m
0.500 kg
350 m,962m
400m
ng s4.
Data Table 3
Calculations Table 3
X1
X2
mg(x2-X1)
V½k(x2²-x1?)
% Diff
7Som 40
700m .480
1.421 1.40 1,4%
1.078 +10373.9%
0.500 kg
7203 +0.6776.2%
650m . SOB
o 600
Le00
0%
3.99 Sl.460)2-(.750)3) =-1.40
1

Transcribed Image Text:Follow-up Questions
4. Instead of comparing changes in energy, compare the total energy at each point. Consider the first
case of the 0.500 kg mass falling from x,=0.250 m to the value of x2 determined for that case. Calculate
M 0.so the sum Uk + Ug at x1 as ½kx1² – mgX1. Now calculate that sum at x2 as 1/2kx22 – mgx2. Compare the two
and comment on the significance of the comparison.
Som
= lo
5. Consider the same case as discussed in question 4. Calculate the value of x halfway between x1 and x2.
Calculate Uk+Ug = ½kx? –mgx for that point. How does it compare with the values calculated in
question 4? Explain the reason for this result.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Help me to solve this problem step by step and please show your answer in exponential format , example exponential format (1.03e3)arrow_forwardYOU MUST SHOW HOW YOU DID THE CONVERSION! Use the above example as a model for your work to show a clear path to answer. A flatbed truck is 35 feet 6 ½ inches long. Convert that distance into mm. 1 inch = 2.54 cm or 1 cm = 0.3937 inch My height is 6 feet 1 inches. I first convert the feet to inches and then add the additional inch. 2.54 cm 10 mmarrow_forwardProblem 2. Planetary Body Composition: Density (Links to an external site.) of the Earth (Palen, et. al., 1st Edition, Chapter 6, problem 70) Earth’s mean (Links to an external site.) radius is 6,378 km and its mass is 5.97 x 1024 kg. CALCULATE Earth’s average (Links to an external site.) density. SHOW YOUR WORK. DO NOT LOOK UP THIS VALUE! The average density of Earth’s crust is 2,600 kg/m3. What does this tell you about Earth’s interior?arrow_forward
- Please help explain what steps I should take to solve this problem. Thank you. (See attached Image)arrow_forwardI need help with knowing what to cirlce. The " increases decreases" part.arrow_forwardPlease explain the answers in easy to understand way. What can you say about the accuracy of your measurements? What can you say about the precision of your measurements? Measure the longest dimension of the room twice, using two different techniques. Do the measurement in feet and inches. Then convert to meters. Below is what I got. Tape Measure - 146 inches > 3.7084 meters / 12 feet and 2 inches = 12.1667 feet > 3.70840 meters Ruler - 144.5 inches (144 + 1/2) = 3.6703 meters / 12.0416 feet = 3.67027 metersarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON