
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
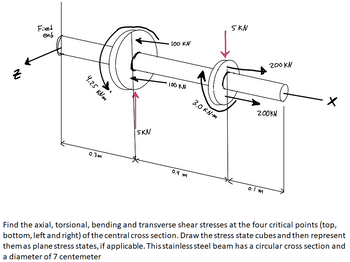
Transcribed Image Text:YU
Fixed
end
4.25 KN.m
0.3m
5KN
· 100 KN
100 KN
0.4 m
3.0 KN-m
5 KN
200 KN
200KN
0.1 m
X
Find the axial, torsional, bending and transverse shear stresses at the four critical points (top,
bottom, left and right) of the central cross section. Draw the stress state cubes and then represent
them as plane stress states, if applicable. This stainless steel beam has a circular cross section and
a diameter of 7 centemeter
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- show all steps/solution plzarrow_forwardFind the max shear stress in a 200mm tall, 150mm wide rectangular cross section using the appropriate reduced shear stress equation. Assume Vmax = 12kN. Find the max shear stress in a W12x50 cross-section using the appropriate estimated shear stress equation. Assume Vmax = 236kips.arrow_forwardFig 1 and 2 pictured with part A calculate the magnitude of the shear stress at the point due to internal shear on the section. calculate the combined normal stress at the point due to internal normal force and the internal bending moment of the section. Answer should be stressarrow_forward
- For the beam shown at right, determine the following: P= 1800 lb a. Maximum tensile bending stress b. Transverse shear stress at a the junction of the "TEE" (i.e., 2" above the neutral axis). c. Transverse shear stress at the neutral axis - 7.5 ft- - 7.5 ft- (a) d. Draw the stress elements -10 in. representing the state of stress at the junction of the “TEE" and at the neutral axis. | 2 in. 4 in. -N- 1600 10 in. 8 in. 42 in.k- (b)arrow_forwardWhat is the maximum length of a uniformly loaded, simply supported beam based on the maximum allowable stresses, its normal stress of 90MPa and its shear stress of 100MPa? The uniform load is 10kN/m. The area is b = 20mm and h = 80mmarrow_forwardThe built-up beam is subjected to a moment of M = 80 kNm. Variable d₁ d₂ d3 da Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. d5 d3 de d₁ Value 128 mm 22 mm 276 mm 11 mm 138 mm d4 12 mm M₁ de d5 a. Determine the distance from the Neutral Axis to the top of the beam, N.A. b. Determine the mass moment of inertia of the beam, I. Determine the max compressive stress acting on the beam, compression c. d. Determine the max tensile stress acting on the beam, tension.arrow_forward
- The simply supported beam shown supports a uniformly distributed load of w = 50 kN/m. Assume x = 1.6 m, a = 3.5 m, b = 6.0 m, xk = 2.5 m. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam are b₁ = 305 mm, t₁ = 23 mm, d = 480 mm, tw = 14 mm, and y = 85 mm. Determine the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress acting at point H. On a piece of paper, show these stresses on an appropriate sketch. ΧΗ พ bf H H B K Ун XK Ук b K a tw darrow_forwardProblem 2 6-53. Determine the moment M that should be applied to the beam in order to create a compressive stress at point D of op 30 MPa. Also sketch the stress distribution acting over the cross section and compute the maximum stress developed in the beam. 25 mm 150 mm 25 mm 25 mm A B 150 mm M 25 mmarrow_forwardA simply supported reinforced concrete beam carries a uniformly distributed load of 12 kN/m on a span of 4 m. The beam has a rectangular cross section 250 mm wide by 450 mm deep, with three 20 mm diameter steel bars placed 60 mm from the bottom of the beam, as shown below. The moduli of elasticity for the concrete and steel are 15 GPa and 200 GPa, respectively. Determine the average tensile stress in the steel and the maximum compressive stress in the concrete at the section of maximum bending moment. 450 mm 250 mm 60 mmarrow_forward
- 2 kip/ft 6 in 10 in B. 40 kip 16 in D. 16 In 5 ft 5 ft 10 ft The simply-supported beam-column above is subjected to a uniformly distributed load and an axial load, as shown. Assume that the Internal resultants on the cross-section passing through point D are as follows: • ND -40 kip • VD 0 Mp = +100 kip-ft Which of the following is closest to the longitudinal normal stress at point D? O-78.1 psi +235 psi O-153 psi O-1.77 ksi H:arrow_forwardq3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY