
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
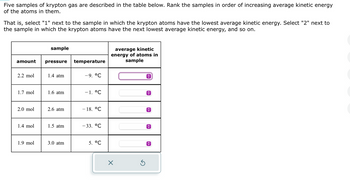
Transcribed Image Text:Five samples of krypton gas are described in the table below. Rank the samples in order of increasing average kinetic energy
of the atoms in them.
That is, select "1" next to the sample in which the krypton atoms have the lowest average kinetic energy. Select "2" next to
the sample in which the krypton atoms have the next lowest average kinetic energy, and so on.
amount
2.2 mol
1.7 mol
2.0 mol
1.4 mol
1.9 mol
sample
pressure
1.4 atm
1.6 atm
2.6 atm
1.5 atm
3.0 atm
temperature
-9. °C
-1. °℃
- 18. °℃
-33. °C
5. °C
average kinetic
energy of atoms in
sample
X
Ś
ŵ
↑
ŵ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider these reactions: Reaction 1: H2(g)+Cl2(g)⟶2HCl(g)ΔH=−184.6 kJ Reaction 2: 2OF2(g)⟶O2(g)+2 F2(g)ΔH=−49.4 kJ Reaction 3: N2(g)+2O2(g)⟶2NO2(g)ΔH=+66.4 kJ Use Reaction 3. How much energy (in kJ) is absorbed when 106. L of nitrogen dioxide is created at STP? Round to the nearest whole number.arrow_forwardPlease answer question 16 part A and Carrow_forwardWhat is the chemical formula for the compound formed between chromium(VI) and chlorine? chemical formula: What is the chemical formula for the compound formed between chromium(VI) and oxygen? chemical formula:arrow_forward
- please see the attached imagearrow_forwardWhen the two atoms are approaching each other, which statement is true about the potential energy (PE) of the system and the kinetic energy (KE) of the atom? A. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increase b. Potential energy increase and kinetic energy decrease c. They both remain constantarrow_forward3. Suppose the 25.0 g of the following substances all initially at 27.0 °C absorb 2.35 kJ of energy. What is the final temperature of each? A) gold B) silver C) Aluminum D) Water. I also needed to look up specific heat values.arrow_forward
- The units for the answer is KJ/mol. But this answer says joules. why is that?arrow_forwardThe First Law of Thermodynamics, known as Conservation of Energy, states that when energy is transformed, the total stays the same. Describe TWO examples of the first law, one involving living organisms and one not involving living organisms.arrow_forwardHess's Law Prelab Questions Name Section 1. A thermometer placed in a solution undergoing a chemical reaction indicates an increase in temperature as the reaction proceeds. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? Describe if heat energy is lost or gained from the reaction (the system) to the surroundings. What is the sign of the enthalpy change (AH) of this reaction? of aola) Goules)arrow_forward
- Use data from table (Figure 1), the figure (Figure 2) and the figure (Figure 3) to calculate the lattice energy of RbClarrow_forwardConsider these reactions: Reaction 1: H2(g)+Cl2(g)⟶2HCl(g)ΔH=−184.6 kJ Reaction 2: 2OF2(g)⟶O2(g)+2 F2(g)ΔH=−49.4 kJ Reaction 3: N2(g)+2O2(g)⟶2NO2(g)ΔH=+66.4 kJ Use Reaction 2. How much energy (in kJ) is released when 79.0 g of oxygen difluoride decomposes?arrow_forwardusing the equations provided, please help me figure out which of them goes to which problems which have also been providedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY