
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Find the pressure drop between locations a and b for flow in a pipe using the following data: Working fluid: Water Pipe: Stainless steel, Schedule No. 120 Nominal pipe size (cm): 10 Flow rate (m3 /min): 2.271 Temperature (C): 38 Length (m): 45.72 Solve for the following 3 cases: a) Za = Zb =33.5 m, b) Za = Zb + 15 m, and c) Za = Zb + 46 m.
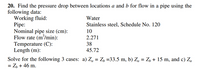
Transcribed Image Text:20. Find the pressure drop between locations a and b for flow in a pipe using the
following data:
Working fluid:
Pipe:
Nominal pipe size (cm):
Flow rate (m'/min):
Temperature (C):
Length (m):
Water
Stainless steel, Schedule No. 120
10
2.271
38
45.72
Solve for the following 3 cases: a) Za = Z, =33.5 m, b) Zą = Z, + 15 m, and c) Za
= Z, + 46 m.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 49. Water flows at a rate of 200 GPM into a piping system connected in series. Length, diameter, and loss coefficient of each pipe are given below. For p= 62.4 Ibm/ft and u = 0.7E–3 lbm ft/s find total pressure drop and the diameter of an equivalent pipe representing this system. C) Fluid Power Theory an.. IndPitEn IlIb. Fluid Mechanics: Incompressible Viscous Flow 392 Pipe D K No. (ft) 100.00 (in) 5.00 (-) 50.00 1 2 80.00 4.50 45.00 3 70.00 4.00 65.00 4 120.00 3.50 55.00 5 90.00 3.00 15.00arrow_forwardFluidarrow_forwardUse g=32.2 */sec2 (9.81 m/s2) and 60°F (16°C) water unless told to do otherwise.• Google schedule-40 pipe’s thickness at different nominal size to obtain the innerdiameter of the pipe for accurate determinaLon of flow velocity.• Must show your work to support your selecLon. Otherwise, no points will be given.• No peer discussion is allowed.1. A schedule-40 pipe necks down from 24 in at point A to 12 in at point B. 8 *3/sec of 60°Fwater flow from point A to point B. The pressure head at point A is 20 *. FricLon is insignificantover the distance between points A and B. What are the magnitude and direcLon of theresultant force on the water? (A) 2900 lbf; toward A(B) 3500 lbf; toward A(C) 2900 lbf; toward B(D) 3500 lbf; toward Barrow_forward
- Solve correctly please, will rate for correct ans only.arrow_forwardcalculate the pressure in the tank. Please solve it fast within 10-20 Minutes (Answer is P_(tank)= 107kPa , Please don't copy-paste other solution)arrow_forwardDescribe the methodology for obtaining the pump curve in a project, where data are collected at five points with different pressures in the pump (10 psi, 15 psi, 20 psi, 25 psi and 30 psi), where to find these Q flow rates a 1000 ml bottle is used and the time needed to fill it is timed, for each of the pump's five pressure points. The gauge pressure H in meters of water column achieved should also be observed, in order to construct the HxQ graph of the pump.arrow_forward
- Solve in simple way ,Must be handwritten only. No Chatgpt.arrow_forward10. Pump/motor E 25m Suction pipe 50mm dia Delivery pipe 50mm dia 142m long 8m long A 2m В Assume: f = 0.008 u in pipe = 2 m/s pump efficiency = 85% motor efficiency = 92% Determine: (i) pressure at C [-31.86 kN/m²] (ii) input power to motor [2.2.kW]arrow_forward% ParametersD = 0.1; % Diameter of the tube (m)L = 1.0; % Length of the tube bundle (m)N = 8; % Number of tubes in the bundleU = 1.0; % Inlet velocity (m/s)rho = 1.2; % Density of the fluid (kg/m^3)mu = 0.01; % Dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa.s) % Define the grid size and time stepdx = D/10; % Spatial step size (m)dy = L/10; % Spatial step size (m)dt = 0.01; % Time step size (s) % Calculate the number of grid points in each directionnx = ceil(D/dx) + 1;ny = ceil(L/dy) + 1; % Create the velocity matrixU_matrix = U * ones(nx, ny); % Perform the iterationsfor iter = 1:100 % Calculate the velocity gradients dUdx = (U_matrix(:, 2:end) - U_matrix(:, 1:end-1)) / dx; dUdy = (U_matrix(2:end, :) - U_matrix(1:end-1, :)) / dy; % Calculate the pressure gradients dpdx = -mu * dUdx; dpdy = -mu * dUdy; % Calculate the change in velocity dU = dt * (dpdx / rho); % Update the velocity matrix U_matrix(:, 2:end-1) = U_matrix(:, 2:end-1) + dU; % Apply…arrow_forward
- Please help, will provide definitely helpful ratings for full solution. Thank uarrow_forwardCompletely solve and box the final answers. Write legibly 9. A blower with the inlet open to the atmosphere delivers 250 cubic meters per minute of air at a pressure of 2.50 cm of water gage through a duct 25 cm in diameter, the manometer being attached to the discharge duct at the blower. Air temperature is 25 degrees C and the barometer pressure reads 1.025 bar. Calculate the required motor rating in KW if the blower efficiency is 92.5%arrow_forwardUse g=32.2 */sec2 (9.81 m/s2) and 60°F (16°C) water unless told to do otherwise.• Google schedule-40 pipe’s thickness at different nominal size to obtain the innerdiameter of the pipe for accurate determinaLon of flow velocity.• Must show your work to support your selecLon. Otherwise, no points will be given.Water flows through a schedule-40 pipe that changes gradually in diameter from 6 in (154mm) at point A to 18 in (429 mm) at point B. The volumetric flow rate is 5.0 *3/sec (130 L/s). The respecLve pressures at points A and B are 10 psia (70 kPa) and 7 psia (48.3 kPa). All lossesare insignificant. What are the direcLon of flow and velocity at point A? (A) 3.2 */sec (1 m/s); from A to B(B) 25 */sec (7.0 m/s); from A to B(C) 3.2 */sec (1 m/s); from B to A(D) 25 */sec (7.5 m/s); from A to Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY