
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
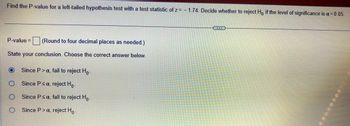
Transcribed Image Text:Find the P-value for a left-tailed hypothesis test with a test statistic of z= -1.74. Decide whether to reject Ho if the level of significance is a = 0.05.
P-value = (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
State your conclusion. Choose the correct answer below.
O
Since P> a, fail to reject Ho-
Since P≤ a, reject Ho-
Since P ≤ a, fail to reject Ho-
Since P> a, reject Ho
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use technology to find the P-value for the hypothesis test described below. The claim is that for 12 AM body temperatures, the mean is μ>98.6°F. The sample size is n=9 and the test statistic is t=2.262.arrow_forwardUse the six steps of hypothesis testing to answer the following question. Remember to determine if the problem is a Z test or T test as that will influence your critical value. You believe you have discovered a topical solution that heals wounds faster. The average number of days it takes to remove stiches after surgery in all hospital patients is 12. In a sample of 29 patients the average number of days to remove stiches is 10.5 with a std dev. Of 1.2 Did your solution lessen the number of days patients had stichesarrow_forwardFind the P-value for a left-tailed hypothesis test with a test statistic of z=−1.33 Decide whether to reject H0 if the level of significance is α=0.05. P-value= Part 2 State your conclusion. Choose the correct answer below. A.) Since P≤α, reject H0. B.) Since P>α, fail to reject H0. C.) Since P≤α, fail to reject H0. D.) Since P>α, reject H0.arrow_forward
- The null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis are: H0: The frequencies are equal.H1: The frequencies are not equal. Category f0 A 10 B 10 C 20 D 10 a. State the decision rule, using the 0.01 significance level. (Round your answer to 3 decimal places.) b. Compute the value of chi-square. (Round your answer to 2 decimal place.) c. What is your decision regarding H0?arrow_forwardAnswer all A, B, C questionsarrow_forwardUse technology to find the P-value for the hypothesis test described below. The claim is that for 12 AM body temperatures, the mean is μ > 98.6 °F. The sample size is n = 3 and the test statistic is t = 1.234.arrow_forward
- Suppase there is a claim that a certaln population has a mean, u, that is less than 9. You want to test this clalm. To do so, you collect a large random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test at the 0.05 level of significance. To start this test, you write the null hypothesis, Hy and the alternative hypothesis, H, as follows. Ho p29 Suppose you also know the following information. The value of the test statistic based on the sample is -1.995 (rounded to 3 decimal places). The p-value is 0.023 (rounded to 3 dedmal places). (a) Complete the steps below for this hypothesis test. O One-tailed o Two-tailed Step 2: Enter the test statistic. (Round to 3 decimal places.) Step 3: Shade the area represented by the p- value. Step 4: Enter the p- value. (Round to 3 decimal places.) (b) Based on your answer to part (a), which statement below is true? Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is rejected. Since the p-value is less…arrow_forwardThe Pavalue for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject Ho when the level of significance is (a) a = 0.01, (b) a = 0.05. and (c)g=0 10 P=0.0816 (a) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.01 level of significance? O A. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0816, is less than a = 0.01. O B. Fail to reject H, because the P-value, 0.0816, is greater than a= 0.01. OC. Reject H, because the P-value, 0.0816, is less than a=0.01. O D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0816, is greater thana= 0.01. (b) Do you reject or fail to reject H, at the 0.05 level of significance? O A. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0816, is less than a =0.05. O B. Fail to reject H, because the P-value, 0.0816, is greater than a= 0.05. OC. Reject H, because the P-value, 0.0816, is greater than oa 0.05. O D. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0816, is less than a = 0,05. (c) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.10 level of significance? O A. Reject Ho because the…arrow_forwardThe p-value for a hypothesis test turns out to be 0.0534. At a 3% level of sigrnificance, what is the proper decision? O Reject Ho O Fail to reject Ho Check Answer e Type here to searcharrow_forward
- Find the P-value for a left-tailed hypothesis test with a test statistic of z = - 1.68. Decide whether to reject H, if the level of significance is a= 0.10. P-value = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) State your conclusion. Choose the correct answer below. O Since P>a, fail to reject Ho- O Since P>a, reject Ho- O Since Psa, fail to reject Ho- OS ince Psa, reject Ho-arrow_forwardDescribe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the indicated claim. A furniture store claims that at least 40% of its new customers will return to buy their next piece of furniture. Describe the type I error. Choose the correct answer below. OA. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece of furniture is at least 0.40, but you fail to reject Ho: p20.40. OB. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece furniture is at least 0.40, but you reject Ho: p20.40. OC. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece of furniture is no more than 0.40, but you reject Ho: p ≤ 0.40. OD. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece f furniture is no more than 0.40, but you fail to reject Ho: p ≤0.40. Describe the type II error. Choose the correct answer…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman