
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
A car is traveling at a constant velocity of magnitude vo when the driver notices a
garbage can on the road in front of him. At that moment, the distance between the
garbage can and the front of the car is d. A time treact after noticing the garbage
can, the driver applies the brakes and slows down at a constant rate before coming
to a halt just before the garbage can. What is the magnitude of the car's
acceleration after the brakes are applied?
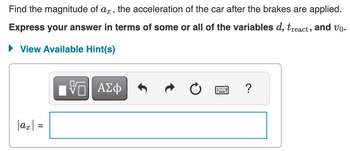
Transcribed Image Text:Find the magnitude of ax, the acceleration of the car after the brakes are applied.
Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables d, treact, and vo.
► View Available Hint(s)
|ax|
||
VE ΑΣΦ
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 9 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
A car is traveling at a constant velocity of magnitude vo when the driver notices a
garbage can on the road in front of him. At that moment, the distance between the
garbage can and the front of the car is d. A time treact after noticing the garbage
can, the driver applies the brakes and slows down at a constant rate before coming
to a halt just before the garbage can. What is the magnitude of the car's
acceleration after the brakes are applied?
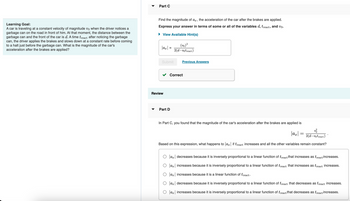
Part C
Find the magnitude of ax, the acceleration of the car after the brakes are applied.
Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables d, treact, and vo.
View Available Hint(s)
|ax|
=
Submit
Review
(vo) ²
2(d-votreact)
Part D
Previous Answers
Correct
In Part C, you found that the magnitude of the car's acceleration after the brakes are applied is
|ax|
v²/
2(d-votreact)
Based on this expression, what happens to |ax| if treact increases and all the other variables remain constant?
=
|ax| decreases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that increases as treact increases.
|ax| increases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that increases as treact increases.
O ax increases because it is a linear function of treact.
O ax decreases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that decreases as treact increases.
|ax| increases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that decreases as treact increases.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
A car is traveling at a constant velocity of magnitude vo when the driver notices a
garbage can on the road in front of him. At that moment, the distance between the
garbage can and the front of the car is d. A time treact after noticing the garbage
can, the driver applies the brakes and slows down at a constant rate before coming
to a halt just before the garbage can. What is the magnitude of the car's
acceleration after the brakes are applied?
Part C
Find the magnitude of ax, the acceleration of the car after the brakes are applied.
Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables d, treact, and vo.
View Available Hint(s)
|ax|
=
Submit
Review
(vo) ²
2(d-votreact)
Part D
Previous Answers
Correct
In Part C, you found that the magnitude of the car's acceleration after the brakes are applied is
|ax|
v²/
2(d-votreact)
Based on this expression, what happens to |ax| if treact increases and all the other variables remain constant?
=
|ax| decreases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that increases as treact increases.
|ax| increases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that increases as treact increases.
O ax increases because it is a linear function of treact.
O ax decreases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that decreases as treact increases.
|ax| increases because it is inversely proportional to a linear function of treact that decreases as treact increases.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Each of the following vectors is given in terms of its x- and y-components. Draw the vector, label an angle that specifies the vector’s direction, then find the vector’s magnitude and direction.a. νx = 20 m/s, νy = 40 m/sb. ax = 2.0 m/s2, ay = -6.0 m/s2arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution...arrow_forwardSomeone drives 215 km west before turning to go 98 km southwest at 45°. How far are they from where they started? Express your answer using three significant figures. 293 km Submit Previous Answers ✓ Correct Part B In what direction are they from where the started, measured counterclockwise from due east?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON