Question
A. Find the kinetic energy K of the car at he top of the loop in Joules.
B. Find the minimum initial height, in meters, at which the car can be released that still allows the car to stay in contact with the track at the top of the loop.
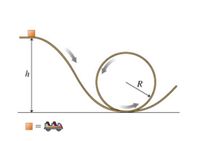
Transcribed Image Text:h

Transcribed Image Text:Loop the Loop
(Figure 1)A roller-coaster car may be represented by a
block of mass 50.0 kg . The car is released from rest at a
height h = 45.0 m above the ground and slides along a
frictionless track. The car encounters a loop of radius R
= 15.0 m at ground level, as shown. As you will learn in
the course of this problem, the initial height 45.0 m is
great enough so that the car never loses contact with the
track.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A daredevil on a motorcycle leaves the end of a ramp with a speed of 33.2 m/s as in the figure below. If his speed is 31.0 m/s when he reaches the peak of the path, what is the maximum height that he reaches? Ignore friction and air resistance. m A daredevil on a motorcyle is at the end of a ramp that is sloped up to the right. An arrow parallel to the ramp's surface is above the daredevil. A dotted-line path traces the trajectory of the daredevil. The path extends up to the right, initially parallel to the surface of the ramp, and decreases in slope until it reaches a maximum, whereupon it extends down to the right with increasing slope magnitude. The vertical distance between the maximum and the highest point of the ramp is h. A horizontal arrow points to the right above the maximum.arrow_forwardQ1. a. Distinguish between homogeneous and non-homogeneous equation. b.Find the work done in moving an object along a straight line from (3, 2, -1) to (2, -1, 4) in a forcefield given by F = 4i – 3j + 2k .arrow_forward. Calculate the potential energy of a 75 Kg boulder sitting at the edge of a cliff that is 210 meters from the ground (yf=0). b. If the boulder is suddenly pushed over the side of the cliff what is the velocity of the boulder when it is 50 meters from the ground?arrow_forward
- For its size, the common flea is one of the most accomplished jumpers in the animal world. A 2.10-mmmm-long, 0.470 mgmg flea can reach a height of 20.0 cmcm in a single leap. Part A Ignoring air drag, what is the takeoff speed of such a flea? Express your answer in meters per second. Part B Calculate the kinetic energy of this flea at takeoff. Express your answer in joules. Part C Calculate the kinetic energy per kilogram of mass. Express your answer in joules per kilogram. If a 77.0 kgkg, 2.00-mm-tall human could jump to the same height compared with his length as the flea jumps compared with its length, how high could the human jump? Express your answer in meters. If a 77.0 kgkg, 2.00-mm-tall human could jump to the same height compared with his length as the flea jumps compared with its length, what takeoff speed would the person need? Express your answer in meters per second. Most humans can jump no more than 60.0 cmcm from a crouched…arrow_forwardThree objects with masses m, = 6.6 kg, m, = 14 kg, and m3 = 16 kg, respectively, are attached by strings over frictionless pulleys as indicated in the fiqure below. The horizontal surface exerts a force of friction of 30 N on m,. If the system is released from rest, use energy concepts to find the speed of m, after it moves down 4.0 m. m/s m2 m1arrow_forward= 13 kg, and m3 20 kg, respectively, are attached by strings over frictionless pulleys as indicated in the figure below. The horizontal surface 3.4 kg, m2 %3D Three objects with masses m, exerts a force of friction of 30 N on m,. If the system is released from rest, use energy concepts to find the speed of m, after it moves down 4.0 m. m/s m2 m1 m3arrow_forward
- a.) A student is riding a bicycle at a constant speed of 6.0 m/s on a level road. The mass of the student and bicycle together is 80 kg. Assume the friction and drag is 35 N. What is the student's output power, in Watts? b.) A student is riding a bicycle at a constant speed of 6.0 m/s on a 7.0º hill. The mass of the student and bicycle together is 80 kg. Assume the friction and drag is 35 N. What is the student's output power, in Watts?arrow_forwardSuppose the object starts from rest, the slide is frictionless and m = 3.50 kg. (Neglect air drag) A. What is the speed of the mass at point B? B. What is the speed of the mass at point C? C. The work done by gravity on the mass as it moves from A to C?arrow_forwardOn a roller coaster ride the total mass of a cart - with two passengers included - is 268 kg. Peak K is at 43.2 m above the ground and peak L is at 26.0 m. At location K the speed of the cart is 17.2 m/s, and at location L it is 12.5 m/s. (The wheel mechanism on roller coaster carts always keeps the carts safely on the rail.) K How much mechanical energy is lost due to friction between the two peaks? Submit Answer Tries 0/10arrow_forward
- An elevator is designed so that when it travels upward, it has constant acceleration from rest to its cruising speed of 2.0 m/s in a time of 4.0 seconds. The elevator has a mass of 625kg. Assume friction is ignored. A. Determine the average power (in W) of the elevator motor while its accelerating upward to its cruising speed. B. Determine the motor power (in W) when the elevator is moving upward at its cruising speed.arrow_forwardA 1250 kg sports car accelerates from zero to 30 m/s in 25 s. What is the average power delivered by the car engine? Select one: a. 25.5 kW b. 22.5 kW с. 12.5 kW Previc ormula Sheet, CA-2, T-3, AY Jump to... 20-21 Activ LENGO toarrow_forwardA sledder has 500 J of potential energy and 230 J of kinetic energy at one point on a steep hill. How much kinetic energy will the sledder have at the bottom of the hill? (Assume negligible air resistance and friction.) b. As the sledder goes down the hill and picks up speed will their potential and kinetic energy increase or decrease.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios