
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Find the following degree of freedom using the formula below
M = 3 (n-1) - j1 - j2
M = Mobility or Total no. of DOF
n = Total no. of links in a mechanism
J1 = No. of joints having 1 DOF
J2 = No. of joints having 2 DOF
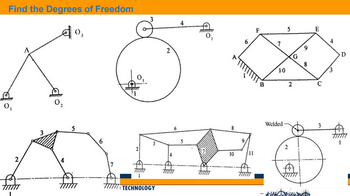
Transcribed Image Text:Find the Degrees of Freedom
40₂
3
monim
form
1
mumew
5
TITITT
7771
o
777777
3
TECHNOLOGY
2
5
mumm
O
777777
10
6
11
777777
F
B
7
10
Welded
2
2
G
TTTTTT
- www
9
8
E
с
3
4
777777
1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- problem 2.5arrow_forwardA camera tripod is set up as shown below. The tripod is pretty fancy and has self-balancing legs. The camera weighs 47 N. Felicia Filmmaker has positioned the tripod as follows: CA=-4 myA=0 m zĄ = 6 m B = -2 myB = 0 m zB = -6 m xc = 6 myc = 0 m zc = -4 m xD = 0 myD = 12 m ZD = 0 m Python input: X_A = -4 y_A = 0 Z_A = 6 X_B = -2 y_B = 0 Z_B = -6 X_C = 6 y_C = 0 Z_C = -4 X_D = 0 y_D = 12 Z_D = 0 Action! A Z number (rtol=0.01, atol=1e-05) number (rtol=0.01, atol=1e-05) number (rtol=0.01, atol=1e-05) y D B --- X Determine the magnitude of the force in each leg of the tripod to keep it in equilibrium: FAD = FBD = FCD = N ? N Narrow_forwardx=8arrow_forward
- Statics with Applications homework problem. Find the forces in the following members using any method. AC, EA, FD, GFarrow_forward1 ONLY ROLLING CONTACT Find the number of links, lower pairs (1-DOF joints), higher pairs (2-DOF joints), and mobility of the mechanism. (See Theory of Machines and Mechanism, 5th Edition, Problem 1.11) (a) n=7, j1-8, j2=1, m=1 (b) n=6, j1=7, j2=1, m-D0 (c) n=8, j1=9, j2=1, m-2 (d) n=7, j1=9, j2=0, m-D0arrow_forwardPlease help explain the annotation?arrow_forward
- Design a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, p = 210°, B-27° for left side and s = 1.24, w= 74°, 2=-40° for right side. Y 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° 2.138 Py Figure 1 Xarrow_forwardI need detailed solution in Handwritten format with diagram. Please don't use chatgpt.arrow_forwardPhotoarrow_forward
- k, k3 A В k2 What is the equivalent spring stiffness between the points A and B. If ki = 1 N/m, k2 =1 N/m. k3 = 2 N/m and k4 = 2 N/m A N/marrow_forwardPlease show tip to tale method steps 4-4. Draw a free-body diagram of member AC in Figure P4-4. to -2 m 3 m A T B C 1 12 50 kN FIGURE P4-4 LOarrow_forwardHi, I have been given this pin-jointed frame analysis to solve (see pictures of the structure attached). Can you help me? The Figure 2 attached is a simplified structure to undertake a structural analysis on a concept design for a low cost stroller/buggy for children. The buggy consists of a number of metal sections that are pin-jointed together. The buggy is designed to accommodate a child of mass no more than 20 kg, sat on the seat which is supported at four points (Fc) on the frame of the buggy. Assume that the weight of the child is equally distributed across all of the points indicated on Figure 2 as Fc. Assume that there are no additional forces applied to the handle of the buggy, that the buggy is static (stationary) and that the buggy, and the elements of the frame have no mass. At points A and G, there are roll supports. At Points B, F and D there are the pin supports. I am required to determine the following: 1) Draw a free-body diagram of the structure 2) Simplify the Free…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY