
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
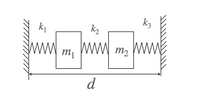
Find the equations of motion for the system, where m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, k1, k2 and k3 are the spring constants of the three springs. In addition, you are given that l1, l2 and l3 are the equilibrium displacements at which spring 1, spring 2, and spring 3 apply zero force, respectively. Lastly, d is the distance between the two rigid walls.
Transcribed Image Text:kz
k1
k2
WWW m2
m1
d
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Don't Use Chat GPT Will Upvotearrow_forward2. A pair of connected pulleys receive a force F = 100 N and P = 150 N as depicted in the image. The radius of pulley 1 is r₁ = 500 mm, and the radius of pulley 2 is r₂ = 950 mm. The pulley system has a radius of gyration of ko = 0.5 m and mass of 50kg. Determine the following: 1. Reaction force in the x direction 2. Reaction force in the y direction 3. Angular acceleration of the pulley F Parrow_forward3kg ball connected to horizontal AB with cable. AB rotates with constant angular velocity w about vertical axis. if angle of cable with vertical is theta= 30 degree, find angular velocity and tension of the cable.arrow_forward
- The frame is subjected to a horizontal force F = {25 j} kN. Apply the learned concepts of forces and equilibrium to compute the components of this force parallel and perpendicular to the member AB. B F= { 25 j } kN 4 m A 3 m 8 marrow_forward4.1.1arrow_forwardQ2/ The out - of - balance of a machine rotor is equivalent to 5 kg at 10 mm radius in one plane A, together with an equal mass at 15 mm radius in a second plane B. AB = 375 mm and the two radii are 120°. Find the mass required in third plane C at a radius of 125 mm and its angular position with respect to the given radii so that there is no resultant out - of - balance force. Find also the position of C along the axis for the residual couple to be a minimum and of this couple when the speed is 500 r.p.m.arrow_forward
- 4qarrow_forwardWrite down the differential equation governing the motion of the system below, where x(t) is the displacement of the system from equilibrium. LEMM in karrow_forward4-22. An airplane travels at a heading of -60° with an air speed of 500mph. The wind is blowing at 30° at a speed of 50mph as shown in Fig. P4:22. Find the speed (magnitude of the velocity vec (V)) and the direction of the plane relative to the ground using vector addition. Check your answer by finding the magnitude and direction using the laws of sines and cosines. Figure P4.22 Velocity of airplane for problem P4 - 22. zbsol 09.49% maldong 500 60° 8 V 50 30°arrow_forward
- Two massless springs with different spring constants k₁= 100 N/m and k₂ = 10 N/m are aligned vertically, as shown in figure 1. A block of mass m = 0.12 kg is placed on the bottom spring. The distance between the top of the box and the top spring is h = 0.35 m. You compress the bottom spring Ay = 0.3 m from its equilibrium position (figure 2). When you let go, the box flies up (figure 3) and compresses the top spring (figure 4). Treat the upward direction (↑) as positive, such that the compression of the top spring is a positive displacement. What is the maximum compression of the top spring due to the flying box? Give your answer in units of meters to 2 decimal places. Use g = 9.8 m/s^2. Assume air resistance is negligible. T h EW Ay (2) www Backup link to image (opens in new tab). fumand M риту 4 ² ↑ M ? wwwarrow_forwardQ3. As shown on the right in image below, the force Facting on the box varies with displacement s, and the coefficient in the image, C = 14. Determine the work done by force Fto the box when the box has displaced s = 1.9 m. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Negative sign must be included if the work done is negative. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. F (N) F 5 3 S 4 C s (m) 1 2arrow_forwardA board sits in equilibrium. On the left end, there is a wire that supports the board from the ceiling, and to the right, there is a sawhorse that supports the board from the ground. The sawhorse is a distance d= 1/5l from the right edge of the board. There is a block with mass ms= 4.5kg that is a distance 3/4l from the right edge of the board. Finally the board has a mass mb= 11kg. c) Write down Newton's 2nd law. Put the equation in terms of mb, ms, g, T, and Fn. Where T is the tension in the wire, and Fn is the normal force of the sawhorse on the board. d) Write down Newton's 2nd Law for rotations. Put the equation in terms of l, mb, ms, g, T, and Fn.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY