
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
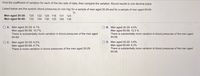
Transcribed Image Text:**Understanding the Coefficient of Variation in Systolic Blood Pressure**
To understand the variation in systolic blood pressure between different age groups, we will find the coefficient of variation for two sets of data. The coefficient of variation (CV) is a statistical measure of the relative variability, expressed as a percentage. It is calculated by dividing the standard deviation by the mean and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
Below are the systolic blood pressures (in mm Hg) for two samples:
- Men aged 20-29: 120, 122, 128, 118, 131, 123
- Men aged 60-69: 132, 154, 136, 125, 164, 139
**Options and Comparisons**
A. Men aged 20-29: 4.1%
Men aged 60-69: 10.7%
There is substantially more variation in blood pressures of the men aged 60-69.
B. Men aged 20-29: 4.0%
Men aged 60-69: 10.3%
There is substantially more variation in blood pressures of the men aged 60-69.
C. Men aged 20-29: 6.5%
Men aged 60-69: 4.7%
There is more variation in blood pressures of the men aged 20-29.
D. Men aged 20-29: 3.8%
Men aged 60-69: 8.3%
There is substantially more variation in blood pressures of the men aged 60-69.
From these options, we compare the coefficients of variation (CVs) of both age groups to determine which one has higher variability in blood pressure and how significant that difference is.
**Explanation and Calculation**
### Steps to Calculate Coefficients of Variation:
1. Calculate the mean (average) systolic blood pressure for each age group.
2. Calculate the standard deviation for each age group.
3. Divide the standard deviation by the mean for each group.
4. Multiply the resulting value by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
Remember:
- Mean = (Sum of all values) / (Number of values)
- Standard deviation measures the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values.
### Conclusion
After performing the necessary calculations based on the given data,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the explained variation, unexplained variation, total variation, coefficient of determination, and standard error of estimate. Round to a minimum of 4 decimal places, if necessary.Eight different second-year medical students took blood pressure measurements of the same patient and the results are listed below. Systolic 131 130 120 139 145 129 146 121 Diastolic 88 96 81 99 98 86 98 79 Explained variation ? Unexplained variation ? Total variation ?arrow_forwardThe amount of trash generated by US households (in lbs per day) is normally distributed. You take a sample of 10 people. The sample average is xbar=10.91 lbs, and the sample standard deviation is s=4.736. What is the 99% Conf. Int. for the mean? Group of answer choices a. 6.04 to 15.78 b. 8.33 to 13.49 c. 8.09 to 13.73 d. 7.74 to 14.08arrow_forwardUse the standard normal table to find the z-score that corresponds to the cumulative area 0.1047. If the area is not in the table, use the entry closest to the area. If the area is halfway between two entries, use the z-score halfway between the corresponding z-scores. Click to view page 1 of the standard normal table. Click to view page 2 of the standard normal table. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- A sample of human brain volumes (cm³) is given below. Use the given data values to identify the corresponding z scores that are used for a normal quantile plot, then identify the coordinates of each point in the normal quantile plot. Construct the normal quantile plot, then determine whether the data appear to be from a population with a normal distribution. 1075 O A. List the z scores for the normal quantile plot. 10 (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use ascending order.) O C. z score z score 321 Identify the coordinates of each point in the normal quantile plot. Use ordered pairs of the form (x,y), where x is the sorted human brain volumes, and y is the corresponding z score. ☐☐☐☐☐☐☐☐ (Type ordered pairs. Round to two decimal places as needed. Use ascending order.) Construct the normal quantile plot. -2- -3- 900 1077 WARU 957 -2- -3+ 900 1026 X Values X Values 1077 1500 1500 Q Q OB. O D. 1443 z score z score Do the data appear to come from a normally distributed population? ܚ ܝ…arrow_forward3.arrow_forwardUse the standard normal table to find the z-score that corresponds to the cumulative area 0.9616. If the area is not in the table, use the entry closest to the area. If the area is halfway between two entries, use the z-score halfway between the corresponding z-scores. Click to view page 1 of the standard normal table. Click to view page 2 of the standard normal table. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.) - X - X Standard normal table (page 1) Standard normal table (page 2) - 3.3 .0004 0005 .0003 .0004 .0004 .0004 .0004 .0004 .0005 .0005 .0005 0.2 .5793 .5832 .5871 .5910 .5948 .5987 .6026 .6064 .6103 .6141 - 3.2 .0005 .0005 .0006 .0006 .0006 .0006 .0006 .0007 .0007 0.3 .6179 .6217 .6255 .6293 .6331 .6368 .6406 .6443 .6480 .6517 3.1 .0007 .0007 .0008 .0008 .0008 .0008 .0009 .0009 .0009 .0010 0.4 .6554 .6591 .6628 .6700 .6736 .6772 .6808 .6844 .6879 .6664 - 3.0 – 2.9 .0010 .0010 .0011 .0011 .0011 .0012 .0012 .0013 .0013 .0013 .6915 .7019 .7088 .7422…arrow_forward
- 00 T R AWM Z. Use the standard normal table to find the z-score that corresponds to the given percentile. If the area is not in the table, use the entry closest to the area. If the area is halfway between two entries, use the z-score halfway between the corresponding z-scores. If convenient, use technology to find the z-score. P72 Cliak to viouno The z-score that corresponds to P72 is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Enter your answer in the answer box. ?. ll Jeffrey Jones 61 Lea V Stop Video Participants Chat Share Screen Record Reactions Unmute Type here to search 近。 PrtScn Home (口 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 23 2$ 5. 9- 4. A. B.arrow_forwardcould you write with a pen and paper?arrow_forwardEstimate the distance traveled in 20 seconds given the following sample velocities using right- endpoint values. Be sure to write the units for your answer. Time (s) 10 15 20 Velocity (m/s) 3 3.4 2.9 2.4 1arrow_forward
- Using the standard normal table in the Toolbox, determine a Z-value. Each response must include three numerical values and be rounded to the hundredths place. Question 1 The cumulative area to Z is 0.80. Question 2 The cumulative area to Z is 0.1762. Question 3 The area between Z and negative infinity is 0.6664. Question 4 The area between Z and positive infinity is 0.119.arrow_forwardThe mean height of women in a country (ages 20 - 29) is 64.3 inches. A random sample of 70 women in this age group is selected. What is the probability that the mean height for the sample is greater than 65 inches? Assume o = 2.86. The probability that the mean height for the sample is greater than 65 inches is (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman