
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
#30) find the absolute extremum, if any, given by the second derivative test for each function
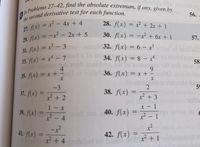
Transcribed Image Text:In Problems 27–42, find the absolute extremum, if any, given by the second derivative test for each function.
27. \( f(x) = x^2 - 4x + 4 \)
28. \( f(x) = x^2 + 2x + 1 \)
29. \( f(x) = -x^2 - 2x + 5 \)
30. \( f(x) = -x^2 + 6x + 1 \)
31. \( f(x) = x^3 - 3 \)
32. \( f(x) = 6 - x^3 \)
33. \( f(x) = x^4 - 7 \)
34. \( f(x) = 8 - x^4 \)
35. \( f(x) = x + \frac{4}{x} \)
36. \( f(x) = x + \frac{9}{x} \)
37. \( f(x) = \frac{-3}{x^2 + 2} \)
38. \( f(x) = \frac{2}{x^2 + 3} \)
39. \( f(x) = \frac{1 - x}{x^2 - 4} \)
40. \( f(x) = \frac{x - 1}{x^2 - 1} \)
41. \( f(x) = \frac{-x^2}{x^2 + 4} \)
42. \( f(x) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1} \)
![### Example 30: Quadratic Function
The given function is:
\[ f(x) = -x^2 + 6x + 1 \]
#### Key Characteristics:
- **Type of Function**: This is a quadratic function, which is a polynomial of degree 2.
- **General Form**: The standard form of a quadratic function is \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \) where \( a = -1 \), \( b = 6 \), and \( c = 1 \).
#### Graphical Representation:
- **Parabola Orientation**: Since the coefficient of \( x^2 \) is negative (\( a = -1 \)), the parabola opens downward.
- **Vertex**: The vertex of the parabola can be found using the formula \( x = -\frac{b}{2a} \).
- **Axis of Symmetry**: This vertical line passes through the vertex, with an equation \( x = -\frac{b}{2a} \).
- **Y-Intercept**: The point where the graph intersects the y-axis, found by evaluating \( f(0) = c \).
#### Additional Analysis:
- **Vertex Form**: The function can be rewritten in vertex form to easily identify the vertex.
- **Roots**: To find the x-intercepts (roots), solve \( f(x) = 0 \).
This function is important for understanding the characteristics of quadratic equations in algebra, including their graphical behavior and real-world applications.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/a8745a0b-010d-470c-8e91-e3a0b1fe773a/ce4bd9ab-b79a-4c34-b503-2fe34620b8b9/2fdn5uk_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:### Example 30: Quadratic Function
The given function is:
\[ f(x) = -x^2 + 6x + 1 \]
#### Key Characteristics:
- **Type of Function**: This is a quadratic function, which is a polynomial of degree 2.
- **General Form**: The standard form of a quadratic function is \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \) where \( a = -1 \), \( b = 6 \), and \( c = 1 \).
#### Graphical Representation:
- **Parabola Orientation**: Since the coefficient of \( x^2 \) is negative (\( a = -1 \)), the parabola opens downward.
- **Vertex**: The vertex of the parabola can be found using the formula \( x = -\frac{b}{2a} \).
- **Axis of Symmetry**: This vertical line passes through the vertex, with an equation \( x = -\frac{b}{2a} \).
- **Y-Intercept**: The point where the graph intersects the y-axis, found by evaluating \( f(0) = c \).
#### Additional Analysis:
- **Vertex Form**: The function can be rewritten in vertex form to easily identify the vertex.
- **Roots**: To find the x-intercepts (roots), solve \( f(x) = 0 \).
This function is important for understanding the characteristics of quadratic equations in algebra, including their graphical behavior and real-world applications.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Don't provide handwriting solutions and answer in detailarrow_forward2. Consider the function f (x) = x¹ − 2x² + 3. (a) Find the intervals on which f is increasing / decreasing. (b) Find the intervals on which f is concave up/ concave down. Display your answer in table form, with a column for the intervals, columns for each factor, a column for the derivative, and a column for the function, as shown in lecture.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following function (image 1) is derivate at the indicated value. If so, indicate the value of the respective derivative. Justify if not is derivate. Value: x=1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning