
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
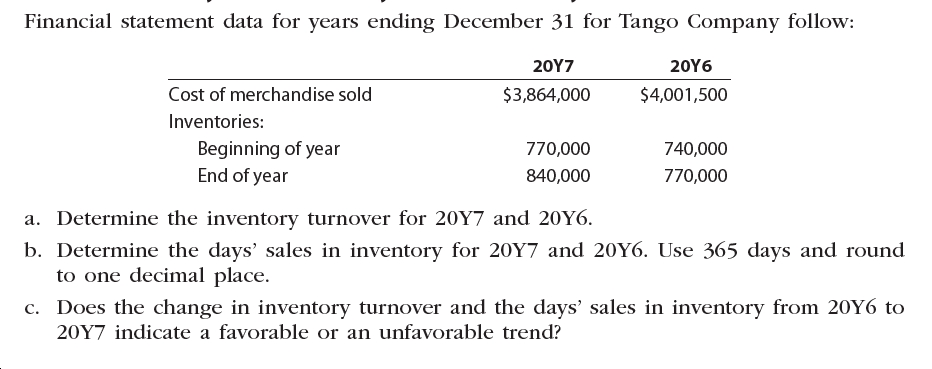
Transcribed Image Text:Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Tango Company follow:
20Υ7
20Υ6
Cost of merchandise sold
$3,864,000
$4,001,500
Inventories:
Beginning of year
End of year
770,000
740,000
770,000
840,000
a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y7 and 20Y6.
b. Determine the days' sales in inventory for 20Y7 and 20Y6. Use 365 days and round
to one decimal place.
c. Does the change in inventory turnover and the days' sales in inventory from 20Y6 to
20Y7 indicate a favorable or an unfavorable trend?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Solve for the missing information designated by "?" in the following table. (Use 365 days in a year. Round the inventory turnover ratio to one decimal place before computing days to sell. Round days to sell to one decimal place.) Case a. b. C. $ $ Beginning Inventory Purchases 112 $ 224 SA Cost of Goods Sold 1,120 $ $ $ 8.0 Days to Sell 36.5arrow_forwardInventory Analysis A company reports the following: Cost of merchandise sold $569,400 Average merchandise inventory 87,600 Determine (a) the inventory turnover and (b) the number of days' sales in inventory. Round interim calculations to the nearest dollar and final answers to one decimal place. Assume 365 days a year. a. Inventory turnover fill in the blank 1 b. Number of days' sales in inventory fill in the blank 2 daysarrow_forwardInventory Analysis A company reports the following: Cost of goods sold $543,120 Average inventory 67,890 Determine (a) the inventory turnover and (b) the number of days' sales in inventory. Round interim calculations to the nearest dollar and final answers to one decimal place. Assume 365 days a year.arrow_forward
- Question Content Area Based on the following data for the current year, what is the inventory turnover (rounded to one decimal place)? Sales on account during year $598,636 Cost of merchandise sold during year 212,753 Accounts receivable, beginning of year 44,419 Accounts receivable, end of year 53,126 Merchandise inventory, beginning of year 32,158 Merchandise inventory, end of year 39,584arrow_forwardInventory turnover and number of days’ sales in inventory Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Tango Company follow: 20Y7 20Y6 Cost of goods sold $3,791,255 $4,079,970 Inventories: Beginning of year 773,800 737,300 End of year 839,500 773,800 Required a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y7 and 20Y6. Round to one decimal place. 20Y7 20Y6 Inventory turnover b. Determine the number of days’ sales in inventory for 20Y7 and 20Y6. Use 365 days and round to one decimal place. 20Y7 20Y6 Number of days’ sales in inventory days days c. Are the changes in inventory turnover and the number of days’ sales in inventory from 20Y6 to 20Y7 favorable or unfavorable?arrow_forward21arrow_forward
- Inventory turnover and 'number of days' sales in inventory Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Tango Company follow: 20Y7 20Υ6 Cost of goods sold $3,739,790 $3,852,940 Inventories: Beginning of year 759,200 722,700 End of year 832,200 759,200 Required a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y7 and 20Y6. Round to one decimal place. 20Υ7 20Y6 Inventory turnover b. Determine the number of days' sales in inventory for 20Y7 and 20Y6. Use 365 days and round to one decimal place. 20Υ7 20Y6 Number of days' sales in inventory days days c. Are the changes in inventory turnover and the number of days' sales in inventory from 20Y6 to 20Y7 favorable or unfavorable?arrow_forwardInventory Turnover and Days Sales in Inventory Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Amsterdam Company follow: 20Y4 2073 Cost of merchandise sold $3,598,900 $3,015,630 Inventories: Beginning of year 593,000 589,600 End of year 648,000 593,000 a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y4 and 20Y3. Round to one decimal place. Inventory Turnover 20Y4 20Y3 b. Determine the days' sales in inventory for 204 and 20Y. Assume 365 days a year. Round interim calculations and final answers to one decimal Days' Sales in Inventory 20Y4 ____ days 20Y3 ____ days c. Does the change in the inventory turnover and the days' sales in inventory from 20Y3 to 204 indicate a favorable or an unfavorable trend?arrow_forwardInventory Turnover and Days’ Sales in Inventory Shown below are data from the Northern Company’s accounting records: Year 1 Year 2 Sales Revenue $8,000,000 $11,000,000 Cost of Goods Sold 4,000,000 4,800,000 Beginning Inventory 510,000 540,000 Ending Inventory 550,000 600,000 Calculate the company’s (a) inventory turnover and (b) days’ sales in inventory for both years.Round your answer to two decimal points. Year 1 Year 2 Inventory turnover Answer Answer Days' sales in inventory Answer Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education