
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
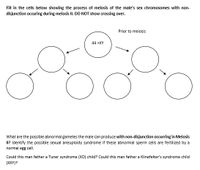
Transcribed Image Text:Fill in the cells below showing the process of meiosis of the male's sex chromosomes with non-
disjunction occuring during meiosis II. DO NOT show crossing over.
Prior to meiosis
44 +XY
What are the possible abnormal gametes the male can produce with non-disjunction occurring in Meiosis
II? Identify the possible sexual aneuploidy syndrome if these abnormal sperm cells are fertilized by a
normal egg cell.
Could this man father a Tuner syndrome (XO) child? Could this man father a Klinefelter's syndrome child
(XXY)?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fill in the blanksarrow_forwardPlease help me with questions 15-21 with details, thank you so much!arrow_forwardIf a female is born with Turner syndrome, how might this have occurred? Draw out the potential scenarios that could lead to this aneuploidy during meiosis focusing on the sex chromosomes and ignoring the other 22 autosomes.arrow_forward
- Please draw the diagram and explain. An organism with a diploid number of 6 reproduces sexually and has heterogametic chromosomes in the male. Diagram the stages of meiosis for gametogenesis in a male of this organism. Make certain you identify homologous pairs of chromosomes.arrow_forwardPut this in order: Many rounds of mitosis occurs to produce a fully grown multicellular organism Meiosis occurs in sex organs to produce gametes. Use this one first- Meiosis occurs producing gametes Two gametes combine in the process of fertilization A diploid zygote is formed MAY 26 tv MacBook Air 吕0 888 DII DD F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 23 2$ % & * 3 4 5 6 7 8. Varrow_forwardPlease explain what would be the consequences in successive generations of offspring if the chromosome number were not reduced during meiosis?arrow_forward
- Give typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forward10:10 E ← sisAndMeiosis.docx FREE EDIT PDF FREE CONVERT PDF TO WORD 2. Why are chromosomes important? 3. How are meiosis I and meiosis II different? 1. What is the state of DNA at the end of meiosis I? What about at the end of meiosis II? 4. Why do you use non-sister chromatids to demonstrate crossing over? 7. Identify two ways that meiosis contributes to genetic recombination. 10. P FREE PDF FILLER 5. What combination of alleles could result from a crossover between BD and bd chromosomes? 8. Why is it necessary to reduce the number of chromosomes in gametes? 6. How many nuclei are present at the end of meiosis II? How many chromosomes are in each? a. Sperm Cell b. Egg Cell AP_5 c. Daughter Cell from Mitosis ON 5G I 9. Blue whales have 44 chromosomes in every cell. Determine how many chromosomes you would expect to find in the following: d. Daughter Cell from Meiosis II COUS ra PAGE 10... FREE CONVERT JPG TO PDF X OeScience Labs, 2016arrow_forwardWhat type of gametes can be produced by simple non-disjunction of the sex chromosomes in a human male? Simple non-disjunction means that non-disjunction occurs in meiosis I or meiosis II, but not in both meiosis I and meiosis II. Choose all answers that are correct Group of answer choices 22, 0 24, YY 25, XXY 23, XX 23, XY 25, XXX 24, XY 24, XXarrow_forward
- A male gamete is formed after non-disjunction during meiosis. This gamete has the normal haploid complement of autosomes but contains both the X and Y chromosomes. This gamete fuses with a normal female gamete containing a haploid autosome set and a single X chromosome.i. If this occurred in Drosophila, what would the sex of the resulting fly be? Justify your answer.ii. If these were human gametes, what would the sex of the resulting zygote be? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardPlease help me!arrow_forwardPlease help me illustrate the stages of meiosis of Ascaris lumbricoides. Anaphase II and Telophase IIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education