
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
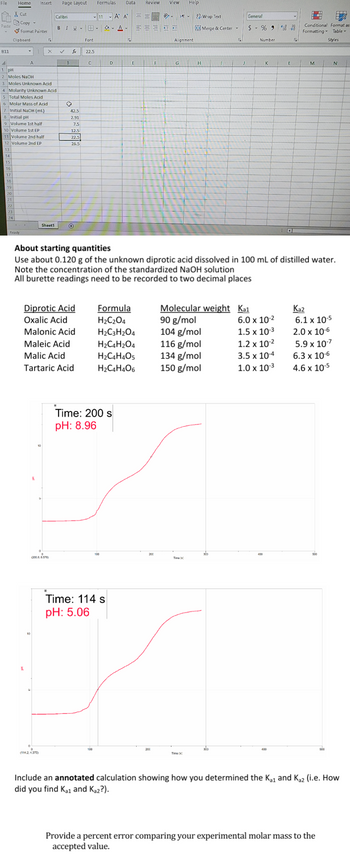
The question and infromation should all be there to answer question. the Answer should be malonic acid
Transcribed Image Text:File
Home
Insert
Page Layout
Formulas Data Review
View
Help
X Cut
Calibri
11 AA
>শ•
Wrap Text
General
Copy
BIU A
Merge & Center
$% 900
Format Painter
Clipboard
E
Font
Alignment.
5
Number
Conditional Format as
Formatting Table▾
Г
Styles
B11
×
✓
fx 22.5
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
1 PH
2 Moles NaOH
3 Moles Unknown Acid
4 Molarity Unknown Acid
5 Total Moles Acid
6 Molar Mass of Acid
+
7 Initial NaOH (mL)
42.5
8 Initial pH
2.91
9 Volume 1st half
7.5
10 Volume 1st EP
12.5
11 Volume 2nd half
22.5
12 Volume 2nd EP
26.5
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
Sheet1
+
Ready
About starting quantities
Use about 0.120 g of the unknown diprotic acid dissolved in 100 mL of distilled water.
Note the concentration of the standardized NaOH solution
All burette readings need to be recorded to two decimal places
H4
Diprotic Acid
Oxalic Acid
Formula
H2C2O4
Molecular weight
Ka1
Ka2
90 g/mol
6.0 x 10-2
6.1 x 10-5
Malonic Acid
H2C3H2O4
104 g/mol
1.5 x 10-3
2.0 x 10-6
Maleic Acid
H2C4H2O4
116 g/mol
1.2 x 10-2
5.9 x 10-7
Malic Acid
H2C4H4O5
134 g/mol
3.5 x 10-4
6.3 x 10-6
Tartaric Acid
H2C4H4O6
150 g/mol
1.0 x 10-3
4.6 x 10-5
(200.8, 8.570)
(114.2.4.375)
Time: 200 s
pH: 8.96
Time: 114 s
pH: 5.06
Time()
Time (s
300
Include an annotated calculation showing how you determined the K₁ and Kǝz (i.e. How
did you find Kai and Ka2?).
Provide a percent error comparing your experimental molar mass to the
accepted value.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 57.0 ml of 0.90 M solution of HCl was diluted by water. The pH of this diluted solution is 0.90. How much water was added to the original solutionInsert your answer rounded to 3 significant figure.arrow_forwardIdentify the conjugate acid for each base. conjugate acid of HS-: conjugate acid of HPO : conjugate acid of NH,: contact us |help abeut us careers privacy policy terms of usearrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] Scoring: Your score will be based on the number of correct matches minus the number of incorrect matches. There is no penalty for missing matches. Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Indicate whether each of the following compounds will give an acidic, basic or neutral solution when dissolved in water. Clear All ammonium chloride potassium hypochlorite potassium chloride ammonium perchlorate Submit Answer Retry Entire Group The pH will be less than 7. The pH will be approximately equal to 7. The pH will be greater than 7. 8 more group attempts remaining Previous Email Instructor Next €3 & Save and Exit COWLarrow_forward
- Pls help ASAP ON ALL ASKED QUESTIONS PLS PLSarrow_forward39. Classify each of the following as a strong acid or a weak acid. H. b. с. а. d.arrow_forwardMatch the terms to the correct definition. (A choice that describes a property of an acid, but is NOT the definition as requested, will be counted as wrong). Substance that donates a proton Brønsted acid Substance that accepts a proton B. v Brønsted base c Substance that causes an increase of [H) in solution Arrhenius acid D. Substance that causes an increase of [OH] in solution Arrhenius base E. Substance that causes a decrease in (H] in solution E. Substance that causes a decrease in (OH] in solution MacBook Air F10 F9 O00 F7 F8 吕0 F5 F3 F4 F1 F2 23 $ % & @ 6 7 8 2 3 4 Q W E R K A S F M. V しー .. エarrow_forward
- Identify if each compound will result in an Acidic, Basic, or Neutral solution. Compound NaBr LICN CaNO3 Acidic, Basic, Neutral [Select] ["Acidic", "Neutral", "Basic"] [Select] ["Acidic", "Basic", "Neutral"] [Select] ["Neutral", "Acidic", "Basic"]arrow_forwardwhereas the strong The difference between a weak acid and a strong acid is that the weak acid ionizes acid ionizes completely, slightly completely, not at all slightly, completely the same slightly, not at allarrow_forwardquestion 23arrow_forward
- No Plagiarism Please! Could someone please Create 2 different acids Models I wrote the formula But do not know how to turn it into a model like the Picture below Popular acid models are Arrhenius model and Bronsted-Lowry model. Arrhenius model According to Arrhenius concept an acid is defined as a substance that contain hydrogen atom and releases hydronium ion in aqueous solution as only cation. For example HCl is an acid according to Arrhenius concept, as it releases H3O+ ion as cation. HCl (aq) +H2O (l)---> H3O+(aq) + Cl- (aq) According to Arrhenius concept a base is defined as a substance that releases hydroxyl ion in aqueous solution as only cation.For example NaOH is a base according to Arrhenius concept, as it releases OH- ion as anion. NaOH (aq) ----> Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Bronsted-Lowry concept According to this concept an acid is defined as a species that releases proton in aqueous solution and forms it's conjugate base. According to this concept a…arrow_forwardIdentify Bronsted-Lowry acid and basearrow_forwardCalculate the values of [H+] and [OH−] using the pH=3 for Vinegar. An increase in pH ofone unit represents how much decrease in hydrogen ion concentration?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY