Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
As shown in Figure P8.10, a green bead of mass 25 g slides along a straight wire. The length of the wire from point Ⓐ︎ to point Ⓑ︎ is 0.600 m, and point Ⓐ︎ is 0.200 m higher than point Ⓑ︎. A constant friction force of magnitude 0.025 0 N acts on the bead. (a) If the bead is released from rest at point Ⓐ︎, what is its speed at point Ⓑ︎? (b) A red bead of mass 25 g slides along a curved wire, subject to a friction force with the same constant magnitude as that on the green bead. If the green and red beads are released simultaneously from rest at point Ⓐ︎ ,which bead reaches point Ⓑ︎ with a higher speed? Explain.
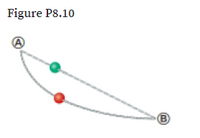
Transcribed Image Text:Figure P8.10
(B)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a girl and her bicycle have a total mass of 60kg. at the top of the hill her speed is 5.0m/s. The hill is 5.0 m high and 100 m long. If the force of friction as she rides down the hill is 20N, what is her speed at the bottom?arrow_forwardA roller coaster starts with a speed of 4.1 m/s at a point 51 m above the bottom of a dip. Neglecting friction, what wil be the speed of the roller coaster at the top of the next slope, which is 30 m above the bottom of the dip? Answer: m/sarrow_forwardA 2.9-kg block with a speed of 4.2 slides down a 7.4-m high, frictionless incline. What is the speed at the bottom?arrow_forward
- The potential energy of a particle as a function of position will be given as U(x) = A x2 + B x + C,where U will be in joules when x is in meters. A, B, and C are constants. What is the force on this particle, in newtons, at x+39cm, if the constants are A= 2.2 J/m^2 , B= 2.2 J/m, and C=6.5 J?arrow_forwardMaria sets up a simple track for her toy block (m = 0.30 kg) as shown in the figure below. She holds the block at the top of the track, 0.54 m above the bottom, and releases it from rest. (a) Neglecting friction, what is the speed of the block when it reaches the bottom of the curve (the beginning of the horizontal section of track)? m/s(b) If friction is present on the horizontal section of track and the block comes to a stop after traveling 0.80 m along the bottom, what is the magnitude of the friction force acting on the block? Narrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution.....arrow_forward
- = 7.50 m. The figure below shows a box with a mass of m = 7.10 kg that starts from rest at point A and slides on a track with negligible friction. Point A is at a height of ha A MET 3.20 m 2.00 m m ha (a) What is the box's speed at point B (in m/s)? m/s What is the box's speed at point C (in m/s)? m/s (b) What is the net work (in J) done by the gravitational force on the box as it moves from point A to point C?arrow_forwardA 145 kg crate slides down a ramp, starting from rest. The ramp is inclined at an angle of 20.6 degrees with respect to the horizontal and has a height of 1.74 m. The crate is placed on frictionless casters so that it slides down the ramp without friction. What is the final speed of the crate (in m/s) just as it reaches the bottom of the ramp? Use g = 9.81 m/s?.arrow_forwardA 2.0kg block starts with a speed of 10. m/s at the bottom of a plane inclined at 35° to the horizontal. The coefficient of sliding friction between the block and the plane is 0.30. use the work-energy theorem to determine how far the block slides along the plane before momentarily coming to rest. I know the answer is 6.2, I just don’t know how to get to it.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios