
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Changes in which factors could cause aggregate
What could happen to the
What could happen to the inflation rate?
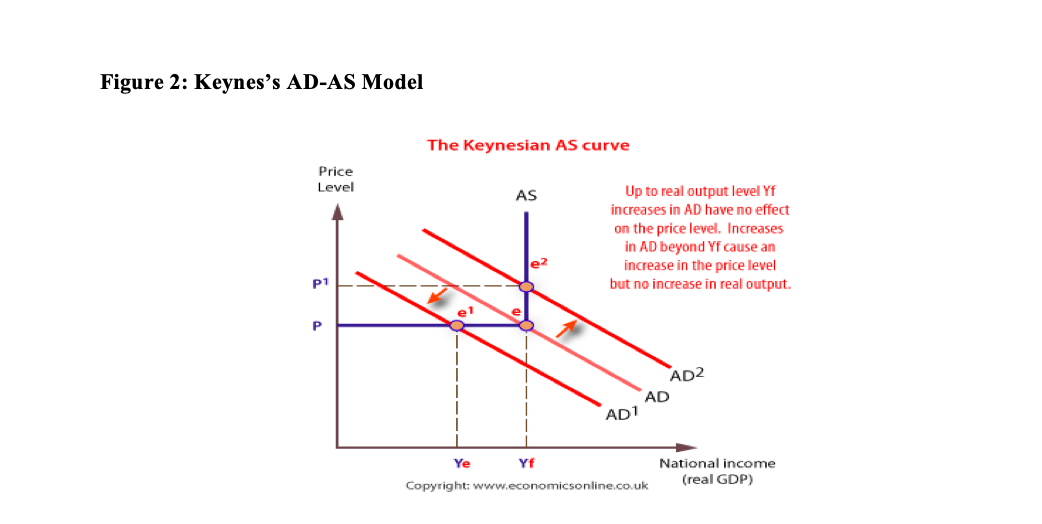
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 2: Keynes's AD-AS Model
The Keynesian AS curve
Price
Level
Up to real output level Yf
AS
increases in AD have no effect
on the price level. Increases
in AD beyond Yf cause an
increase in the price level
but no increase in real output.
p1
AD2
AD
AD1
National income
(real GDP)
Copyright: www.economicsonline.co.uk
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Economists forecast future economic conditions by studying variables that tend to fluctuate in advance of the overall economy. The most significant of these variables are known as leading indicators, and they compose the index of leading economic indicators. Which of the following variables are measured as part of this index? Check all that apply. Supplier deliveries The ratio of elderly to nonelderly workers New orders for consumer goods Stock prices The money supply True or False: Businesses and government care only about long-run economic forecasts, because they cannot adapt policy or output to accommodate short-run fluctuations. False True Suppose the most recent data show that the average initial weekly claims for unemployment insurance have recently decreased. This change suggests ____ period in the coming months.arrow_forwardInflation has reached its highest point since the 1970s. Please identify at least three factors affecting AS and/or AD, and briefly explain the final combined effect of these factors on real GDP and inflation.Include at least one factor affecting AS and at least one factor affecting AD.arrow_forwardWhat relationship does the short-run aggregate supply curve represent?arrow_forward
- A rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve with no change in the aggregate demand curve signals an economic expansion. True or False?arrow_forwardExplain two ways in which a recession might raise the natural rate of unemployment (Macroeconomics field of question)arrow_forwardEmpirical studies indicate that the long-run trend in real GDP of the USA has an upward trend. How is this possible given business cycles and macroeconomic fluctuations? What factors explain the upward trend despite the cycles?arrow_forward
- If the labor force of 160 million people is growing by 1.2 percent this year, how many new jobs have to be created each month to keep unemployment from increasing?arrow_forwardUsing the AD-AS model, if consumers and business become more optimistic about the future direction of the economy and increase spending, then: a-long-run aggregate supply will decrease. b-aggregate demand will decrease. c-aggregate demand will increase. d-long-run aggregate supply will increase.arrow_forwardGraph an economy which suffers a negative supply shock. How does this effect inflation (increase/decrease) and unemployment (increase/decrease)? What is the name for this situation? What is the relationship between unemployment and inflation as the economy heads into a recession normally? How about the relationship as the economy moves to the peak of the business cycle?arrow_forward
- Suppose that an economy wants to boost available labor hours in order to increase aggregate supply. What is the best way to accomplish this?arrow_forwardUse two graphs in the AD-AS framework to compare and contrast demand-pull and cost-push inflation. How do their causes differ? How do the outcomes (inflation, output, employment) differ?arrow_forwardWhy is it difficult to accurately measure the unemployment rate in the U.S.? Do you think the current unemployment rate is overstated, understated, or exactly right?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education