
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172364
Author: Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
None
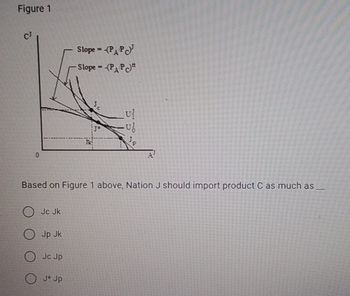
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 1
CJ
Slope = -(PAP)
Slope =-(PAP)"
U
Jk
0
Based on Figure 1 above, Nation J should import product C as much as
Jc Jk
Jp Jk
Jc Jp
J* Jp
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Why do low-income countries like Brazil, Egypt, or Vietnam have lower environmental standards than high-income countries like the Germany, Japan, or the United States?arrow_forwardIn Japan, one worker can make 5 tons of rubber or 80 radios. In Malaysia, one worker can make 10 tons of rubber or 40 radios. Who has the absolute advantage in the production of rubber or radios? How can you tell? Calculate the opportunity cost of producing 80 additional radios in Japan and in Malaysia. (Your calculation may involve fractions, which is fine,) Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of radios? Calculate the opportunity cost of producing 10 additional tons of rubber in Japan and in Malaysia. Which country has a comparative advantage in producing rubber? In this example, does each country have an absolute advantage and a comparative advantage in the same good? In what product should Japan specialize? In what product should Malaysia specialize?arrow_forwardWhat is splitting up the value chain?arrow_forward
- Are differences in geography behind the differences in absolute advantages?arrow_forwardHow does protectionism affect the price of the protected good in the domestic market?arrow_forwardSuppose we extend the circular flow model to add imports and exports. Copy the circular flow diagram onto a sheet of paper and then add a foreign county as a third agent. Draw a rough sketch of the flows of imports, exports, and the payment for each on your diagram.arrow_forward
- France and Tunisia both have Mediterranean climates that are excellent for producing/harvesting green beans and tomatoes. In France it takes two hours for each worker to harvest green beans and two hours to harvest a tomato. Tunisian workers need only one hour to harvest the tomatoes but four hours to harvest green beans. Assume there are only two workers, one in each country, and each works 40 hours a week. Draw a production possibilities frontier for each country. Hint: Remember the production possibility frontier is the maximum that all workers can produce at a unit of time which, in this problem, is a week. Identify which country has the absolute advantage in green beans and which country has the absolute advantage in tomatoes. Identity which country has the comparative advantage. How much would France have to give up In terms of tomatoes to gain from trade? How much would it have to give up in terms of green beans?arrow_forwardHow can governments identify good candidates for infant industry protection? Can you suggest some key characteristics of good candidates? Why are Industries like computers not good candidates for infant industry protection?arrow_forwardWhy might Belgium, France, Italy, and Sweden have a higher export to GDP ratio than the United States?arrow_forward
- Are the gains from international trade more likely to be relatively more important to large or small countries?arrow_forwardIn Germany it takes three workers to make one television and four workers to make one video camera. In Poland It takes six workers to make one television and 12 workers to make one video camera. Who has the absolute advantage in the production of televisions? Who has the absolute advantage in the production of video cameras? How can you tell? Calculate the opportunity cost of producing one additional television set in Germany and In Poland. (Your calculation may involve fractions, which Is tine.) Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of televisions? Calculate the opportunity cost of producing one video camera in Germany and in Poland. Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of video cameras? In this example, is absolute advantage the same as comparative advantage, or not? In what product should Germany specialize? In what product should Poland specialize?arrow_forwardDoes intra-industry trade contradict the theory of comparative advantage?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...
Economics
ISBN:9781337091985
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning