
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Two thin disk-shaped wheels of radii RA = 40 cm and RB = 60 cm are attached to each other on an axle that passes through the center.
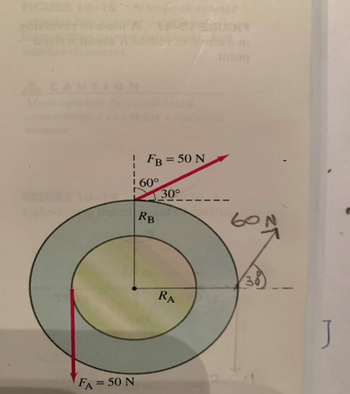
Transcribed Image Text:cas no
FB = 50 N
! 60°
FA = 50 N
RB
30°
RA
60N
(38)
J
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A bicyclist notes that the pedal sprocket has a radius of rp = 8.5 cm while the wheel sprocket has a radius of rw = 6.5 cm. The two sprockets are connected by a chain which rotates without slipping. The bicycle wheel has a radius R = 64 cm. When pedaling the cyclist notes that the pedal rotates at one revolution every t = 1.8 s. When pedaling, the wheel sprocket and the wheel move at the same angular speed. a. Calculate the angular speed of the pedal sprocket ωp, in radians per second. b. Calculate the linear speed of the outer edge of the pedal sprocket vp, in centimeters per second. c. Calculate the angular speed of the wheel sprocket ωw, in radians per second. d. Calculate the linear speed of the bicycle v, in meters per second, assuming the wheel does not slip across the ground.arrow_forwardIn the figure, two 6.90 kg blocks are connected by a massless string over a pulley of radius 1.10 cm and rotational inertia 7.40 x 10-4 kg-m². The string does not slip on the pulley; it is not known whether there is friction between the table and the sliding block; the pulley's axis is frictionless. When this system is released from rest, the pulley turns through 0.900 rad in 148 ms and the acceleration of the blocks is constant. What are (a) the magnitude of the pulley's angular acceleration, (b) the magnitude of either block's acceleration, (c) string tension T1, and (d) string tension T2? Assume free-fall acceleration to be equal to 9.81 m/s?. (a) Number i Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Units >arrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forward
- Question 16 my m, Two blocks are joined by a pulley system (see Figure). The pulley is a solid disk of mass 0.5 kg and radius 179 mm. Assume that the pulley rotates smoothly. If mass 1 is 4.4 kg and mass 2 is 15 kg, what is the angular acceleration of the disk? HINT: the tensions in the horizontal and vertical portions of the rope are not equal. (PUHQ1629)arrow_forwardA wheel has a radius of 3.00 m. How far (path length) does a point on the circumference travel if the wheel is rotated through the following angles, respectively? (a) 25.0° (b) (c) m 25.0 rad 25.0 rev marrow_forwardIn the figure, two 5.70 kg blocks are connected by a massless string over a pulley of radius 140 cm and rotational inertia 7.40 x 104 kg-m². The string does not slip on the pulley: it is not known whether there is friction between the table and the sliding block; the pulley's axis is frictionless. When this system is released from rest, the pulley turns through 1.20 rad in 126 ms and the acceleration of the blocks is constant. What are (a) the magnitude of the pulley's angular acceleration, (b) the magnitude of either block's acceleration, (c) string tension T, and (d) string tension T;? Assume free-fall acceleration to be equal to 9.81 ms?. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Units >arrow_forward
- In the figure, two 6.30 kg blocks are connected by a massless string over a pulley of radius 1.30 cm and rotational inertia 7.40 x 104 kg-m2. The string does not slip on the pulley; it is not known whether there is friction between the table and the sliding block; the pulley's axis is frictionless. When this system is released from rest, the pulley turns through 0.800 rad in 126 ms and the acceleration of the blocks is constant. What are (a) the magnitude of the pulley's angular acceleration, (b) the magnitude of either block's acceleration, (c) string tension T,, and (d) string tension T,? Assume free-fall acceleration to be equal to 9.81 m/s. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Unitsarrow_forwardIn the figure below, two 7.00 kg blocks are connected by a massless string over a pulley of radius 1.30 cm and rotational inertia 3.50 x 10-4 kg · m2. The string does not slip on the pulley; it is not known whether there is friction between the table and the sliding block; the pulley's axis is frictionless. When this system is released from rest, the pulley turns through 0.150 rad in 90.0 ms, and the acceleration of the blocks is constant. T, T (a) What is the magnitude of the pulley's angular acceleration? rad/s2 (b) What is the magnitude of either block's acceleration? m/s2 (c) What is the string tension T? N (d) What is the string tension T2? Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON