
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
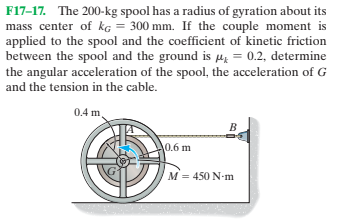
Transcribed Image Text:F17-17. The 200-kg spool has a radius of gyration about its
mass center of kg = 300 mm. If the couple moment is
applied to the spool and the coefficient of kinetic friction
between the spool and the ground is He = 0.2, determine
the angular acceleration of the spool, the acceleration of G
and the tension in the cable.
0.4 m.
0.6 m
M = 450 N-m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The 16-kg wheel is rolling under the constant moment of M = 60 N-m. The wheel has radius r= 0.50 m, has mass center at point G, and the radius of gyration is kg = 0.23 m. The coefficients of friction between the wheel and the ground is ls = 0.28 and Uk = 0.14. If the wheel rolls without slipping, determine the angular acceleration of the wheel (in rad/s?). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. Marrow_forwardThe wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration KG=0.4 m. The spring's unstretched length is Lo=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is 8-30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is 8-0°. The spring's length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (10) The kinetic energy at the state1?__ (N-m) (two decimal places) LLLLLLL L₂ State 2 C State 1arrow_forwardThe wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration kG=0.4 m. The spring’s unstretched length is L0=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is θ=30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is θ=0°. The spring’s length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. Ignore the spring's mass. (5) At state 2, how long the spring is stretched from its unstretched state (length difference):________(m) (two decimal places) (6) The elastic potential energy of the spring at the state 2 is_______(N·m) (two decimal places) (7) The instantaneous center of zero velocity (IC) of the wheel at state 1 is (8) The mass moment of inertial of the wheel about its mass center G is IG =_________(kg·m2 ) (two decimal places) (9) The mass moment of inertial of the wheel about its…arrow_forward
- The wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration kG=0.4 m. The spring’s unstretched length is L0=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is θ=30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is θ=0°. The spring’s length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (1) If the mass center G is set as the origin (datum), the gravitational potential energy at the state 1 is___ (two decimal places) (2) If the mass center G is set as the origin (datum), the gravitational potential energy at the state 2 is___ (two decimal places) (3) The stretched spring length of the spring at the state 1 is________(m) (two decimal places) (4) The elastic potential energy at the potion 1 is_______(N·m) (two decimal places) (5) The stretched spring length of the spring at the…arrow_forwardThe wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration kG=0.4 m. The spring’s unstretched length is L0=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is θ=30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is θ=0°. The spring’s length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (9) The mass moment of inertial about the IC center is IIC =_________(kg·m2 ) (two decimal places)arrow_forwardThe 136-kg spool has a radius of gyration about its mass center of kg = 300 mm. If the couple moment is applied to the spool and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the spool and the ground is u: = 0.2, determine the angular acceleration of the spool, the acceleration of G and the tension in the cable. (Figure 1) Part B Determine the acceleration of G. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ac = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part C Figure Determine the tension in the cable. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0.4 m В HA 0.6 m T = Value Units M = 450 N-m Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- The wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration KG=0.4 m. The spring's unstretched length is Lo=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is 8-30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is 8=0°. The spring's length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (11) The angular velocity at the state 2?_ _(rad/s) (two decimal places) 111441 L₂ State 2 State 1arrow_forwardThe shown spool has a mass of 450 kg and aradius of gyration Gk=1.2 m. It rests on thesurface of conveyer belt for which the coefficient offriction m= 0.5. If the conveyer acceleratesat2 1.2m / S and the spools rolls without slipping,determine the tension in the wire and the angularacceleration of the spoolarrow_forwardThe wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration kG=0.4 m. The spring’s unstretched length is L0=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is θ=30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is θ=0°. The spring’s length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (1) If the mass center G is set as the origin (datum), the gravitational potential energy at the state 1 is___ (two decimal places)arrow_forward
- Pravinbhaiarrow_forwardThe wheel is attached to the spring. The mass of the wheel is m=20 kg. The radius of the wheel is 0.6m. The radius of gyration ke=0.4 m. The spring's unstretched length is Lo=1.0 m. The stiffness coefficient of the spring is k=2.0 N/m. The wheel is released from rest at the state 1 when the angle between the spring and the vertical direction is 8-30°. The wheel rolls without slipping and passes the position at the state 2 when the angle is 8=0°. The spring's length at the state 2 is L2=4 m. (3) The stretched spring length of the spring at the state 1 is_ places) 2₂ State 2 7717 State 1 _(m) (two decimalarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY