
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
The attached figure shows a gas contained in a vertical piston– cylinder assembly, where D = 10 cm. A vertical shaft whose cross-sectional area is 0.8 cm2 is attached to the top of the piston. The total mass of the piston and shaft is 25 kg. While the gas is slowly heated, the internal energy of the gas increases by 0.1 kJ, the potential energy of the piston–shaft combination increases by 0.2 kJ, and a force of F = 1668 N is exerted on the shaft as shown in the figure. The piston and cylinder are poor conductors, and friction between them is negligible.The local atmospheric pressure is 1 bar and g = 9.81 m/s2. (Patm = 1 bar)
Determine, (a) the work done by the shaft, (b) the work done in displacing the atmosphere, and (c) the heat transfer to the gas, all in kJ.
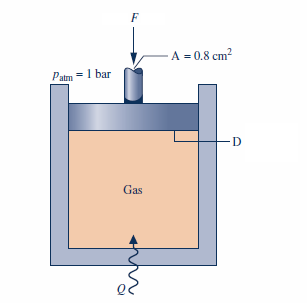
Transcribed Image Text:F
- A = 0.8 cm2
Patm = 1 bar
D
Gas
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 320-N child is in a swing that is attached to a pair of ropes 2.20 m long. Find the gravitational potential energy of the child-Earth system relative to the child's lowest position at the following times. (a) when the ropes are horizontal (b) when the ropes make a 26.0° angle with the vertical (c) when the child is at the bottom of the circular arc Jarrow_forwardTwo electric pumps are being used to pump water to a cistern at the top of a 50 meter hill. A meter is used to measure the electrical energy in kWh consumed by both pumps over a six-hour period. Both pumps consume the same kWh of electrical energy over the pumping period. If we know that pump #1 has an efficiency of 40% and pump #2 has an efficiency of 80%, what can we say about the volume of water moved by each pump? Assume both pumps use the same piping system, so hydraulic frictional losses are the same for both pumps. pump #1 moved twice as much water as pump #2 pump #2 moved twice as much water as pump #1 both pumps moved the same amount of waterarrow_forwardThe piston of a vertical piston-cylinder device containing a gas has a mass of 50 kg and a cross- sectional area of 0.04 m2, as shown in the figure. The local atmospheric pressure is 0.97 bar, and the gravitational acceleration is 9.81 m/s². What is the pressure inside the cylinder?arrow_forward
- The figure below shows a spherical buoy, having a diameter of 1.7 m and weighing 6500 N, anchored to the floor of a lake by a cable. The density of the lake water is 10³ kg/m³ and g = 9.81 m/s². Determine the force exerted by the cable, in N. Water p = 10³ kg/m³ Buoy Cablearrow_forwardA torque of 2 N-m is necessary to rotate a paddle wheel at a rate of 20 rad/s.The paddle wheel is located in a rigid vessel containing a gas. What is the net work injoule done on the gas during 10 minutes of operation?arrow_forwardCalculate the spring constant, k, in kN/m.arrow_forward
- The boom of a fire truck raises a fireman (and his equipment—total weight 280 lbf) 40 ft into the air to fight a building fire. (a) Showing all your work and using unity conversion ratios, calculate the work done by the boom on the fireman in units of Btu. (b) If the useful power supplied by the boom to lift the fireman is 3.50 hp, estimate how long it takes to lift the fireman.arrow_forwardA gas is contained in a vertical piston-cylinder assembly by a piston with a face area of 60 in2 and weight of 100 lbf. The atmosphere exerts a pressure of 14.7 lbf/in² on top of the piston. A paddle wheel transfers 3 Btu of energy to the gas during a process in which the elevation of the piston increases slowly by 2 ft. The piston and cylinder are poor thermal conductors, and friction between the piston and cylinder can be neglected. Determine the work done by the gas on the piston, in Btu, and the change in internal energy of the gas, in Btu. Step 1 Determine the expansion work done by the gas on the piston, in Btu. Wexp = i Btuarrow_forwardAn electric boiler generates 100,000 Btus of heat. Roughly, what is the electrical input of the boiler (in other words, the electrical energy to produce the output), in kilo-watts?arrow_forward
- A firearm can be modeled as a kind of heat engine, where the projectile acts as a piston that separates from the rest of the system during expansion. Consider a rifle with a 1.70 kg barrel made of iron [specific heat = 448 J/(kg °C)]. The rifle fires a 4.00 g bullet that exits the barrel with a speed of 350 m/s. When the propellant is ignited, 1.10% of the energy released goes into propelling the bullet (this is the thermal efficiency of the "engine"). The other 98.9% can be approximated as being entirely absorbed by the barrel, which increases in temperature uniformly for a short time before this energy is dissipated into the surroundings. What is this temperature increase (in °C)? (Round your answer to at least one decimal place.) °℃arrow_forwardFor a gas of volumes Vi = 9.50 10-4 m3 and Vf = 1.40 10-4 m3 and pressures Pi = 2.00 106 Pa and Pf = 2.05 107 Pa, answer the following.For an isobaric process at Pi, find the internal energy change of the gas during this process.For an isovolumetric process at Vi, find the internal energy change of the gas during this process.arrow_forwardI need help on thisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY