
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Friction on the concrete surface creates a couple moment of MO = 100 N ⋅ m on the blades of the trowel. Determine the magnitude of the couple forces so that the resultant couple moment on the trowel is zero. The forces
lie in the horizontal plane and act perpendicular to the handle of the trowel.
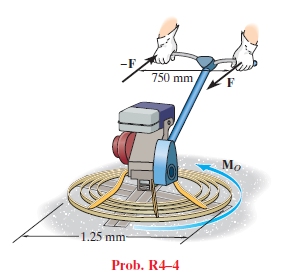
Transcribed Image Text:-F
750 mm F
Mo
1.25 mm
Prob. R4-4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 10.0 m long ladder weighing 50.0 N rests against a smooth vertical wall. If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when it makes a 50.0° angle with the ground find the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and ground. The ladder is in equilibrium. This means that the torque around ANY pivot point must be zero. In problems like this, you can pick the pivot point of your choice, and still solve for the correct forces. However, there is typically a choice for the pivot point that makes the problem solving steps possible or at least easier. This will depend on the problem, but often depends on the fact that the torque due to a force at the pivot point is zero. This lets you ignore those torque terms in your calculations. a. What is the best choice of pivot point for this problem? Select one: A. The base of the ladder B. The center of mass of the ladder C. The top of the ladder By selecting the base of the ladder, you can ignore the torque due to both the…arrow_forwardA war-wolf, or trebuchet, is a device used during the Middle Ages to throw rocks at castles and now sometimes used to fling pumpkins and pianos. A simple trebuchet is shown in the figure below. Model it as a stiff rod of negligible mass 3.00 m long and joining particles of mass m₁ = 0.120 kg and m₂ = 55.0 kg at its ends. It can turn on a frictionless horizontal axle perpendicular to the rod and 15.5 cm from the particle of larger mass. The rod is released from rest in a horizontal orientation. Find the maximum speed that the object of smaller mass attains when it leaves the trebuchet horizontally. m/s m₂ Need Help? Read It 3.00 m m₂ earrow_forwardForce F = (8.55 N )î – (9.95 N )ê acts on a pebble with position vector T (6.87 m )ĵ – (2.53 m )k, relative to the origin. What is the resulting torque acting on the pebble about (a) the origin and (b) a point with coordinates (8.02 m, 0, - 6.52 m)?arrow_forward
- If the pole makes an angle of 25° with the horizontal, the distance between the point where the line is attached to the pole and the anglers hand is L = 2.45 m, and the fish pulls on the line such that the tension in the line is T = 166 N at an angle 35.0° below the horizontal, determine the magnitude (in N · m) of the torque exerted by the fish about an axis perpendicular to the page and passing through the angler's hand.arrow_forwardA potter's wheel having a radius 0.48 m and a moment of inertia of 10.5 kg · m2 is rotating freely at 50 rev/min. The potter can stop the wheel in 4.0 s by pressing a wet rag against the rim and exerting a radially inward force of 69 N. Find the effective coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheel and the wet rag.arrow_forwardForce F = (-7.0 N)î + (5.0 N) ĵ acts on a particle with position vector7 = (4.0 m)î + (5.0 m) ĵ. (a) What is the torque on the particle about the origin, in unit-vector notation? = N: m (b) What is the angle between the directions of r and Torque is the cross product of a position vector (extending from a chosen point, here the origin, to the particle) and a force vector. Did you take the cross product in unit-vector notation? Do you remember how find the angle between two vectors by taking a dot product in both unit-vector notation and also in magnitude-angle notation? (You can similarly use a cross product to do this.) Do you remember how to find the magnitude of a vector from its components?arrow_forward
- A potter's wheel having a radius 0.51 m and a moment of inertia of 14.9 kg · m2 is rotating freely at 50 rev/min. The potter can stop the wheel in 7.0 s by pressing a wet rag against the rim and exerting a radially inward force of 74 N. Find the effective coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheel and the wet rag.arrow_forwardyo-yo with an inner cylinder of r = 3.5 cm and outer radius of R = 6.50cm is at rest on a theta = 30 degree incline. Itis held in place by friction and the tension in the string that is wrapped around its inner cylinder, as shown in the figure. Assume that the positive x-direction points down the incline. Determine the friction force if the mass of the yo-yo is 420g.arrow_forwardWhile installing new spark plugs in your car, the manual specifies they be tightened to 74 Nm. If you can only apply a force to the wrench 21 cm from the plug, and only at an angle of 53 degrees, What magnitude force should you apply to the wrench?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON