
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Two boxes are connected by a lightweight (mass-less!) cord & are resting on a smooth (frictionless!) table. The masses are mA =10 kg & mB = 3 kg. A horizontal force F = 80 N is applied to mA. Calculate:
- Acceleration of the boxes.
- Tension in the cord connecting the boxes.
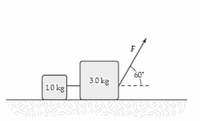
Transcribed Image Text:60
3.0 kg
10 kg
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
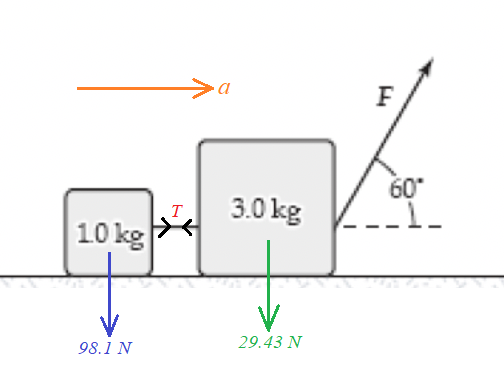
Step 1
Given:
Mass mA = 10 kg.
Mass mB = 3.0 kg.
Force F = 80 N.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When you lift an object by moving only your forearm, the main lifting muscle in your arm is the biceps. Suppose the mass of a forearm with hand is 1.60 kg. If the biceps is connected to the forearm a distance of 2.2 cm from the elbow, how much force must the biceps exert to hold a 39 N ball at the end of the forearm at distance of 36.0 cm from the elbow, with the forearm parallel to the floor, in Newtons? Use g = 10.0 m/s2. Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forwardA 55 kg box is sitting on a rubber conveyor belt. The friction angle is reported to be 38o, what is the maximum acceleration the belt can have to avoid having the box slip along the conveyor?arrow_forwardTwo identical strings making an angle of 0 = 30° with respect to the vertical support a block of mass m = 15.0 kg (see below). What is the tension in each of the strings?arrow_forward
- 11. The sketch shows a painter's scaffold in mechanical equilibrium. The person in the middle weights 250 N, and the tensions in each rope are 200 N. What is the weight of the scaffold? 200 N Ad 250 N *W=? א 200 12. A cue striker a billiard ball, exerting an average force of 23 Newtons over a time of 14 milliseconds. If the ball has mass 0.36-kg, what speed it have after impact ?arrow_forwardWhen you lift an object by moving only your forearm, the main lifting muscle in your arm is the biceps. Suppose the mass of a forearm with hand is 1.60 kg. If the biceps is connected to the forearm a distance of 2.4 cm from the elbow, how much force must the biceps exert to hold a 42 N ball at the end of the forearm at distance of 36.0 cm from the elbow, with the forearm parallel to the floor, in Newtons? Use g = 10.0 m/s2. Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forwardWhen you lift an object by moving only your forearm, the main lifting muscle in your arm is the biceps. Suppose the mass of a forearm with hand is 1.60 kg. If the biceps is connected to the forearm a distance of 2.1 cm from the elbow, how much force must the biceps exert to hold a 35 N ball at the end of the forearm at distance of 36.0 cm from the elbow, with the forearm parallel to the floor, in Newtons? Use g = 10.0 m/s2. Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forward
- A tutor told me that the answer to 1b was 10N but I don't understand why it would be 10N for the tension. If that is correct could someone break it down for me?arrow_forwardHi I needed help with this. An athlete with a mass of 53.5 kg is doing pushups as shown in the figure below. The value for rW⊥ is 1.00 m and the value for rR⊥ is 1.60 m. (a) Assuming she moves upward at a constant speed, determine the force she must exert on the floor with each hand to do a push-up.(b) The triceps muscle in the back of her upper arm with an effective lever arm of rT⊥ = 1.70 cm, as shown in the figure below, and she exerts force on the floor a horizontal distance of r 'R⊥ = 2.05 cm from the elbow joint. Determine the force in the triceps muscle.In order to appreciate the strength of the triceps, determine the ratio of the force in the tricep muscle to her weight (in decimal form). FT/W = ?arrow_forwardThe block in the figure below has a mass of 5.9 kg and it rests on an incline of angle 0. m 07 You pull on the rope with a force F = 38 N. Assume the incline is smooth and determine the angle of the incline if th moves with constant speed.arrow_forward
- | The drawing shows an outstretched arm (0.61 m in length) that is parallel to the floor. The arm is pulling downward against the ring attached to the pulley system, in order to hold the 98-N weight *75. stationary. To pull the arm downward, the latissimus dorsi muscle applies the force M in the drawing, at a point that is 0.069 m from the shoulder joint and oriented at an angle of 29°. The arm has a weight of 47 N and a center of gravity (cg) that is located 0.28 m from the shoulder joint. Find the magnitude of M. 0.61 m 0.28 m 0.069 m Axis at 98 N shoulder joint cg 29arrow_forwardPlease, explain it step-by-step process.arrow_forwardThe pulley and all surfaces are frictionless. Suppose both blocks are made of solid gold. In addition, each block has a mass of 2.38 kg. Find the tension (in N) in the connecting the two gold blocks. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON