
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
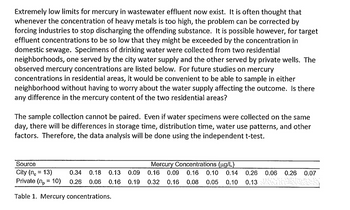
Transcribed Image Text:Extremely low limits for mercury in wastewater effluent now exist. It is often thought that
whenever the concentration of heavy metals is too high, the problem can be corrected by
forcing industries to stop discharging the offending substance. It is possible however, for target
effluent concentrations to be so low that they might be exceeded by the concentration in
domestic sewage. Specimens of drinking water were collected from two residential
neighborhoods, one served by the city water supply and the other served by private wells. The
observed mercury concentrations are listed below. For future studies on mercury
concentrations in residential areas, it would be convenient to be able to sample in either
neighborhood without having to worry about the water supply affecting the outcome. Is there
any difference in the mercury content of the two residential areas?
The sample collection cannot be paired. Even if water specimens were collected on the same
day, there will be differences in storage time, distribution time, water use patterns, and other
factors. Therefore, the data analysis will be done using the independent t-test.
Source
City (n = 13)
Private (n = 10)
Table 1. Mercury concentrations.
0.34 0.18 0.13 0.09
0.26 0.06 0.16 0.19
Mercury Concentrations (µg/L)
0.16 0.09 0.16 0.10 0.14 0.26 0.06 0.26 0.07
0.32 0.16 0.08 0.05 0.10 0.13
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 1) You test a new drug to reduce blood pressure. A group of 15 patients with high blood pressure report the following systolic pressures (measured in mm Hg): before medication: after medication: change: ̄y s187 120 151 143 160 168 181 197 133 128 130 195 130 147 193 157.53 27.409 187 118 147 145 158 166 177 196 134 124 133 196 130 146 189 156.40 27.060 0 2 4 -2 2 2 4 1 -1 4 -3 -1 0 1 4 1.133 2.295 a) Calculate a 95% CI for the change in blood pressure. b) Calculate a 99% CI for the change in blood pressure. c) Does either interval (the one you calculated in (a) or (b)) include 0? Why is this important? d) Now conduct a one sample t-test using μ = 0, and α = .05. Are the results consistent with (a)? Why or why not? e) Finally, conduct a one sample t-test using μ = 0, and α = .01. Are the results consistent with (b)? Why or why not?arrow_forward1) You test a new drug to reduce blood pressure. A group of 15 patients with high blood pressure report the following systolic pressures (measured in mm Hg): y before medication: 187 120 151 143 160 168 181 197 133 128 130 195 130 147 193 157.53 27.409 after medication: 187 118 147 145 158 166 177 196 134 124 133 196 130 146 189 156.40 27.060 change: 0 2 4 -2 2 2 4 1 -1 4 -3 -1 0 1 4 1.133 2.295 a) Calculate a 95% CI for the change in blood pressure. b) Calculate a 99% CI for the change in blood pressure. c) Does either interval (the one you calculated in (a) or (b)) include 0? Why is this important? d) Now conduct a one sample t-test using u = 0, and a = .05. Are the results consistent with (a)? Why or why not? e) Finally, conduct a one sample t-test using u = 0, and a = .01. Are the results consistent with (b)? Why or why not? (Make sure you answer the part in bold for (d) and (e). See also problem 5)arrow_forward1. Susan Sound predicts that students will learn most effectively with a constant background sound, as opposed to an unpredictable sound or no sound at all She randomly divides twenty-four students into three groups of eight. All students study a passage of text for 30 minutes. Those in group 1 study with background sound at a constant volume in the background. Those in group 2 study with noise that changes volume periodically. Those in group 3 study with no sound at all. After studying, all students take a 10 point multiple choice test over the material. Their scores follow test scoresS group 7 46 86 629 5 5 3 4 4 7 2 2 2 471 2 1 5 5 1) constant sound 2) random sound 3) no soundarrow_forward
- State the type of variable in each of the following cases 1- 5.1. The weight (Kg) of an Amazon package.2. The stress level (Low, Average, High) of a student taking this exam.3. The number of Long Covid-19 patients in England in 2021.4. Type of vaccine (Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Moderna).5. The annual profits (£m) of the JSA company in 2021.Your answer should be A, or B or C or D, where A, B, C, and D are defined asfollows:A. Numerical and DiscreteB. Numerical and ContinuousC. Categorical and NominalD. Categorical and Ordinalarrow_forwardAlex hypothesized that, on average, students study less than the recommended two hours per credit hour each week outside of class. Which of the following is Alex's alternative hypothesis? Choose the correct answer below. O A. H₁: μ=2 hours per week per credit O B. H₁: μ #2 hours per week per credit O C. H₁: μ2 hours per week per creditarrow_forwardNote: Use a computer application (SPSS) to solve for the following problems.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman