
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
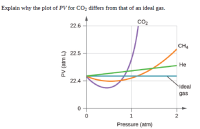
Transcribed Image Text:Explain why the plot of PV for CO2 differs from that of an ideal gas.
CO2
22.6
CH4
I 22.5
Не
22.4
Ideal
gas
1.
2
Pressure (atm)
PV (atm L)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4. Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas: Mg + HCl → H₂ + MgCl₂ (ac) If 2.30 g of Mg is reacted with an excess amount of HCI at SATP, what volume of hydrogen gas will be produced? Show as much work as possible.arrow_forwardWhen 50. g of solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) sublimes 28.6 kJ of heat are required. How much heat would be needed to produce 57 g of carbon dioxide gas from the sublimation of dry ice? CO₂ (s)→ CO₂ (8)arrow_forwardDefine specific heat capacity. the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a substance by 1°C the quantity of heat required to change a system's temperature by 1°C the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°F the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 liter of a substance by 1°Carrow_forward
- I need help with question 80?arrow_forwardA substance, X, has the following properties. SpecificHeat Capacities Hvap 20. kJ/mol C(s) 3.0 J/g°C Hfus 5.0 kJ/mol C(l) 2.5 J/g°C bp 75°C C(g) 1.0 J/g°C mp -15°C Calculate the energy that must be removed to convert 250. grams of the substance X from a gas at 114°C to a solid -45.1°C. Assume X has a molar mass of 75.0 g/mol.arrow_forwardI need help with question 74?arrow_forward
- Aluminum chloride, a white powder, is an important chemical produced industrially by heating a mixture of aluminum metal and chlorine gas. Write a balanced molecular equation with physical states for what has just been described. Predict the theoretical yield of aluminum chloride, in moles, when 351 g of aluminum metal are put in presence of 1,310 g of chlorine. Show all work. If the reaction was carried out at 650 °C, what volume would the original amount of chlorine have occupied at 10.0 bar? Show all work.arrow_forwardGas is trapped inside of a cell with volume 150 m3. The gas exerts 7300 Pa of pressure against the walls of the cell. A machine then expands the cell and gives off 290 kJ of heat to the gas during the process. If the internal energy changed by 97 kJ, what is the final volume of the cell? Assume the pressure stays constant. 120 m3 210 m3 97 m3 180 m3 200 m3arrow_forwardAssuming constant pressure, a gas has a final volume of 15 L. If the temperature increases from 330 K to 450 K, find the initial volume. Show all work in the space provided, and then write your final answer on the short line.arrow_forward
- 21 Consider the combustion of in oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. In an experiment, 0.1063 g of C₅H₈ is combusted to produce enough heat to raise the temperature of 150.0 g of water by 7.632 °C. C₅H₈ (l) + 7 O₂ (g) → 5 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O (g) d If 4790 J of heat were absorbed by the water, then how much heat, in J, was produced by the combustion of C₅H₈? (include the appropriate sign)arrow_forwardWrite a balanced thermochemical equation with phase labels for the Haber process with the heat energy as part of the equation.arrow_forward1a. Calculate the pressure of a sample of 1 mole of argon gas in a 0.1500 L flask at -10.2 ℃ using the ideal gas law and the Van der Waals equation. The a value for argon is 1.34 (L 2 ∙ atm/mol2 ) and the b value is 0.0322 (L/mol). Show all work Ideal pressure= ? real pressure =? 1b.Why is there a difference in the real gas pressure and the ideal pressure? Explain what assumption(s) of the kinetic molecular theory of gases break down under these conditions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY