
Exercises:
1. Evapotranspiration rate is an imporant ecological and climatological variable. It describes how fast water is being evaporated from Earth’s surface and transpired by vegetation. Thus it describes the rate at which moisture is supplied to the atmosphere from the land. The evapotranspiration rate (or ET for short) usually cannot be estimated directly, and instead is calculated from the difference between the rates of rainfall (or P for short) and runoff (or R for short). (Note: the expression below assumes that recharge and discharge to groundwater are in balance, so that there are no changes in storage.)
ET = P – R
At the Birkenes watershed in southern Norway, 16 years of monitoring data indicate that annual rainfall is 1483±265 mm/yr (
(a) If this was all you knew (i.e., if you knew nothing about whether the rainfall and runoff were correlated positively or negatively, and so assumed they were uncorrelated), what would you estimate to be the mean and the standard deviation of annual ET at this site?
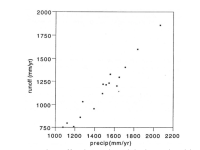
(b) Contrary to your assumption in (a), rainfall and runoff are highly correlated here (see graph below). In fact, the
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- What was the maximum sustained yield under the logistic harvest model when k=500 and r=0.4? Values 1 500 1000 49L K L N N.d num [1:601] 0 123456789... num [1:50] 5 157.502 1079.678 0.732 24.054 ... num [1:50] 114 329 349 350 350 ... 0.4 int [1:50] 1 2 3 45678910 50 t Nt r Z Z L P T time y Files Plots Packages Help Viewer Presentation Zoom Export num [1:601] 0.4 0.399 0.398 0.398 0.397 ... Publish Observed Growth Rate 69 -0.1 0.1 0.3 0.5 Observed Growth Maximum Growth Carrying Capacity 0 100 200 300 400 500 600arrow_forward10.23. Question. An umbrella-shaped island has a population of 499 healthy people. Alice, who is injected with the T-virus, enters the island on day 0. It is known that anyone infected with the T-virus will become a zombie after 24 hours. Assume that the infected (zombies are considered infected) will spread the virus (through biting) and no one on this island can escape from it. The rate of virus transmission is proportional to the product of the number of infected and non-infected. Thus, if x(t) denotes the number of the infected on day t, then dx dt = kx(500 — x). On day 10, it is observed that 20 people are already infected. Answer the following questions. (a) How many zombies are on the island on day 16? (b) On day 20, how many people are infected but not yet turned into a zombie? (c) A rescue boat with 50 available seats is to be sent to the island. What is the earliest day the boat should be sent to ensure it can rescue all survivors (those not infected)?arrow_forward4. Please help me answer this question we’ll calculate and explained. A stone is thrown from the top of a 200 m cliff. The height of the stone relative to the ground is represented by the formula (shown in the image). The time t is in seconds and the height h in meters. A) Calculates its initial speed (instant variation rate at 0s.). B) Calculates the average rate of change for the first two seconds. C) Calculates the rate of instantaneous change at 2 seconds. D) From the results obtained in a), b) and c), describe the displacement of the stone.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





