
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
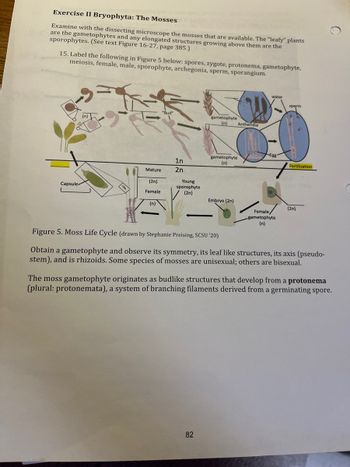
Transcribed Image Text:Exercise II Bryophyta: The Mosses
Examine with the dissecting microscope the mosses that are available. The "leafy" plants
are the gametophytes and any elongated structures growing above them are the
sporophytes. (See text Figure 16-27, page 385.)
15. Label the following in Figure 5 below: spores, zygote, protonema, gametophyte,
meiosis, female, male, sporophyte, archegonia, sperm, sporangium.
Capsule
(n)
9
"Bud"
Mature
(2n)
Female
(n)
1n
2n
Young
sporophyte
(2n)
gametophyte
(n)
82
Antheridia
gametophyte
(n)
Embryo (2n)
water
E88
Female
-gametophyte
(n)
sperm
Fertilization
(2n)
Figure 5. Moss Life Cycle (drawn by Stephanie Preising, SCSU '20)
Obtain a gametophyte and observe its symmetry, its leaf like structures, its axis (pseudo-
stem), and is rhizoids. Some species of mosses are unisexual; others are bisexual.
The moss gametophyte originates as budlike structures that develop from a protonema
(plural: protonemata), a system of branching filaments derived from a germinating spore.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question:- Fill in the blank: Selaginella produces roots like other vascular plants, but it also has roots that arise from ________ on the plant.arrow_forwardThe table please?arrow_forwardExercise II: Monilophyta Part A: Ferns The ferns differ from other seedless vascular plants in their possession of megaphylls, larger leaves with multiple veins. Examine the many living fern sporophytes. There is much diversity in megaphyll morphology. (See also text Figures 17-23, 24, 26, and 36, pages 413, 414, 416, and 424). Identify the frond, the rhizome, and the roots. Most fern fronds are compound, with the blade divided into separate leaflets. If young leaves are present, notice how they unfold. These young leaves are often called fiddleheads. Examine the leaves for the presence of sporangia. Notice if they are grouped together in sori (singular: sorus), distributed evenly over the lower surface of the leaf, or in other patterns. The sporangia of some species may be protected by specialized outgrowths of the leaf called indusia (singular: indusium) (See text Figure 17-32, page 420). 6. Is the indusium diploid or haploid?. Obtain a small square of a fern leaf with one associated…arrow_forward
- carpels and seeds: Berry n ; single seed and apery, floral tube sed to ovary wall Fruit Lab Review Questions Attach the Table from the Bryophyte Lab with all of the columns filled in comparing Bryophytes, Ferns, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms. 1. What is (are) the function(s) of fruit? 2. From what structure (s) do fruits develop? 3. Give an example of a fruit that is dry at maturity, that people generally eat while it is still immature (fleshy). Name 4. Give an example of a fleshy fruit that is partially derived from the receptacle? 5. In most fruits, the ovary wall develops into what 3 layers? 139 141arrow_forward2 Use the internet or your textbook (search with index) to explore the difference in the structure of monocot and dicot plants (why are they different and how can you visually distinguish them when looking at a plant)Identify at least 3 differences and write your findings in your notebooks, noting the source of your information ( text, website address etc.).arrow_forwardNot sure how to solve thisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education