
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
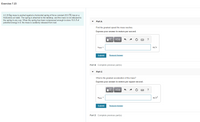
Transcribed Image Text:Exercise 7.23
A 2.20 kg mass is pushed against a horizontal spring of force constant 26.0 N/cm on a
frictionless air table. The spring is attached to the tabletop, and the mass is not attached to
the spring in any way. When the spring has been compressed enough to store 15.0 J of
potential energy in it, the mass is suddenly released from rest.
Part A
Find the greatest speed the mass reaches.
Express your answer in meters per second.
nνα ΑΣφ
?
Umax =
m/s
Submit
Request Answer
Part B Complete previous part(s)
Part C
What is the greatest acceleration of the mass?
Express your answer in meters per square second.
Πνα ΑΣφ
?
Amax =
m/s²
Submit
Request Answer
Part D Complete previous part(s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A net force along the z-axis that has a-component F₂ = -12.0 N + (0.300 N/m²) x² is applied to a 4.50 kg object that is initially at the origin and moving in the -x- direction with a speed of 8.70 m/s. Part A What is the speed of the object when it reaches the point x = 7.60 m? Express your answer with the appropriate units. _O ī Submit μÀ Value Request Answer Units ?arrow_forwardA 2.85 kg block on a horizontal floor is attached to a horizontal spring that is initially compressed 0.0340 m. The spring has force constant 860 N/m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the block is 0.380. The block and spring are released from rest and the block slides along the floor. Part A What is the speed of the block when it has moved a distance of 0.0170 m from its initial position? (At this point the spring is compressed 0.0170 m.) Express your answer with the appropriate units. v= O ΕΞΑ Value Units ?arrow_forward7.53arrow_forward
- You drop a ball from a height of 1.8 m , and it bounces back to a height of 1.2 m Part C What is the ball's speed just after the bounce? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? Vafter = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part D Where did the energy go? O The energy "lost" was changed primarily into thermal energy due to friction. O The energy "lost" was changed primarily into heat energy. The energy "lost" was changed primarily into acoustic energy. O The energy "lost" was changed primarily into chemical energy.arrow_forwardA force in the +z-direction with magnitude 18.0 N- (0.530 N/m)z is applied to a 6.60 kg box F(x) that is sitting on the horizontal, frictionless surface of a frozen lake. F(x) is the only horizontal force on the box. O Part A If the box is initially at rest at r = 0, what is its speed after it has traveled 16.0 m ? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? HA Value Units Submit Previous Answers Request Answerarrow_forwardWhat's the answer for all the parts?arrow_forward
- Using energy considerations, calculate the average force (in N) a 63.0 kg sprinter exerts backward on the track to accelerate from 2.00 to 7.00 m/s in a distance of 25.0 m, if he encounters a headwind that exerts an average force of 30.0 N against him. N Additional Materials O Readingarrow_forwardA 2.6 kg block is attached to a horizontal rope that exerts a variable force Fx = (20 – 5x) N, where x is in m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor is 0.25. Initially the block is at rest at x = 0 m. Part A What is the block's speed when it has been pulled to x = 0.80 m? V = μĂ Value m S ?arrow_forwardPM1.1 please explain each steparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON